Translate this page into:
Chemical Peels for Melasma in Dark-Skinned Patients
Address for correspondence: Dr. Rashmi Sarkar, Department of Dermatology, Maulana Azad Medical College, and Lok Nayak Hospital, New Delhi, India. E-mail: rashmisarkar@yahoo.com
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This article was originally published by Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Abstract
Melasma is a common disorder of hyperpigmentation, which has a severe impact on the quality of life. Inspite of tremendous research, the treatment remains frustrating both to the patient and the treating physician. Dark skin types (Fitzpatrick types IV to VI) are especially difficult to treat owing to the increased risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). The treatment ranges from a variety of easily applied topical therapies to agents like lasers and chemical peels. Peels are a well-known modality of treatment for melasma, having shown promising results in many clinical trials. However, in darker races, the choice of the peeling agent becomes relatively limited; so, there is the need for priming agents and additional maintenance peels. Although a number of new agents have come up, there is little published evidence supporting their use in day-to -day practice. The traditional glycolic peels prove to be the best both in terms of safety as well as efficacy. Lactic acid peels being relatively inexpensive and having shown equally good results in a few studies, definitely need further experimentation. We also recommend the use of a new peeling agent, the easy phytic solution, which does not require neutralisation unlike the traditional alpha-hydroxy peels. The choice of peeling agent, the peel concentration as well as the frequency and duration of peels are all important to achieve optimum results.
Keywords
Chemical peels
dark skin
melasma
INTRODUCTION
Melasma is an acquired disorder of hyperpigmentation characterised by blotchy, light-to-dark brown macules distributed symmetrically on the sun-exposed parts of the body.[12] It is seen predominantly in Fitzpatrick skin types IV-VI, especially among Hispanics, African Americans, Africans and Asians.[12] The disorder has a severe impact on the quality of life, causing deep psychological and social stress. Despite tremendous research into the etiology, pathogenesis and possible treatment options for melasma, the disease remains a therapeutic challenge to dermatologists, and a definitive modality of treatment is still a distant reality.
ETIOLOGY AND PATHOGENESIS
Although many factors have been proposed to have a role in pathogenesis, the exact cause and etiology are yet to be understood. The most commonly identifiable risk factors include ultraviolet radiation, genetic predisposition, pregnancy, oral contraceptives, thyroid disease and drugs like antiepileptics.[2–6] The excessive pigmentation has been attributed to both melanocytosis (increased number of melanocytes) as well as melanogenesis (excess production of melanin) as confirmed by Kang et al.[7] in a histopathological study on Asian patients. Furthermore, a vascular component has also been proposed to play a role in the pathogenesis of melasma. Kim et al.[8] have found that biopsy specimens of lesional melasma skin had greater expression of the vascular endothelial growth factor in keratinocytes compared to nearby nonlesional skin.
CLINICAL AND HISTOLOGICAL TYPES
Three distinct facial patterns have been traditionally identified for melasma: Malar, centrofacial and mandibular. Although melasma of the arms and forearms has also been described, the entity is relatively uncommon and less characterised than facial melasma.[910] Regarding the histological classification of melasma, three histologic patterns have been identified based on the primary location of pigment accumulation: Epidermal, dermal and mixed.[1112]
TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR MELASMA
As regards management, the therapeutic options range from photoprotection, topical hypopigmenting agents, chemical peels and lasers to a variety of less-tried systemic agents like fish oil, green tea and deoxyarbutin.[13–15] Although no single agent has proved to be effective for all patients, a combination of two or three agents is often tried to achieve optimum results. Inspite of this, the treatment of melasma remains a challenge, and a mild-moderate improvement is all that is achieved in a majority of patients.
MELASMA IN DARK SKIN
Although dark skin (Fitzpatrick type IV to VI) confers better photoprotection to photodamage, it is by itself a risk factor for pigmentary disorders like melasma. Moreover, its tendency for post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) is a major limiting factor for treatment procedures like lasers and chemical peels. The high incidence of PIH in darker skin is attributed to its faulty pathophysiological response to cutaneous injury, owing, in turn, to its increased melanocyte activity.[16] Hence, the prevention and management of PIH after the application of various agents including chemical peels are of prime importance while treating melasma in dark skin.
CHEMICAL PEELS FOR MELASMA
Chemical peeling is the application of a chemical agent to the skin, which causes the controlled destruction of a part or of the entire epidermis, with or without the dermis, leading to exfoliation and removal of superficial lesions, followed by the regeneration of new epidermal and dermal tissues.[17] Chemical peels are a well-known modality of treatment for melasma. The basic mechanism of the action of chemical peels in melasma is the removal of unwanted melanin by causing a controlled chemical burn to the skin.[13] Peels have proved to be useful agents for melasma both as a sole treatment as well as an adjunct to other topical therapies.
CHEMICAL PEELS FOR MELASMA IN DARK SKIN
Although a wide variety of agents are available for chemical peels, the choice becomes relatively limited when you are treating a patient with a Fitzpatrick skin type IV or above.[18] This is because the deep chemical peels cannot be used in dark-skinned patients owing to the risk of prolonged hyperpigmentation.[1618] Even medium-depth peels need to be used with extreme caution. A list of agents which can be used for peeling in darker skin types is summarised in Table 1.

Furthermore, chemical peels are generally used to treat only the epidermal and mixed forms of melasma, as an attempt to treat the deeper variant often leads to unwanted complications like hypertrophic scarring and permanent depigmentation.
Alpha hydroxy peels
Glycolic acid (GA) peelis the most commonly used alphahydroxy peel. It is generally used as a 30-70% GA solution. After a test peel, serial glycolic peels are applied to the face at an interval of 2-3 weeks, for a duration of 3-5 minutes. The peel is then neutralised using water or 1% bicarbonate solution. There have been ample studies using GA for melasma in ethnic skin [Table 2]. In most of these studies, there was a moderate improvement achieved in almost one-half of the patients.[19–22] As expected, the epidermal form showed the best response, followed by the mixed type, whereas the dermal variant was almost resistant to the effect of chemical peels.[21] GA peels have also been compared with other agents like topical hypopigmenting agents, lasers and other peels [Table 3]. In one of our own studies, we tried to assess the effect of the addition of serial GA peels to a time-tested regime, the Kligman's formula. Forty Indian melasma patients were divided into two groups of 20 each. One group received serial GA peels (30% for the first three sittings and 40% for the next three sittings) combined with the modified Kligman's formula. The other received only the modified Kligman's formula. A significant decrease in the Melasma Area Severity Index (MASI) score from baseline to 21 weeks was observed in both groups (P < .001). However, the group receiving the GA peels showed more rapid and greater improvement, with statistically significant results (P < .001).[26] The only sideeffects observed with the GA peels were mild burning, erythema, desquamation and a transient PIH. In contrast to our study, Hurley et al.[27] observed no added benefit with a combination of GA peels and 4% hydroquinone as compared to 4% hydroquinone alone. However, in this study on 21 Hispanic women, the concentration of GA used was low (20-30%), which could be a reason for this deviation in results observed by the authors.
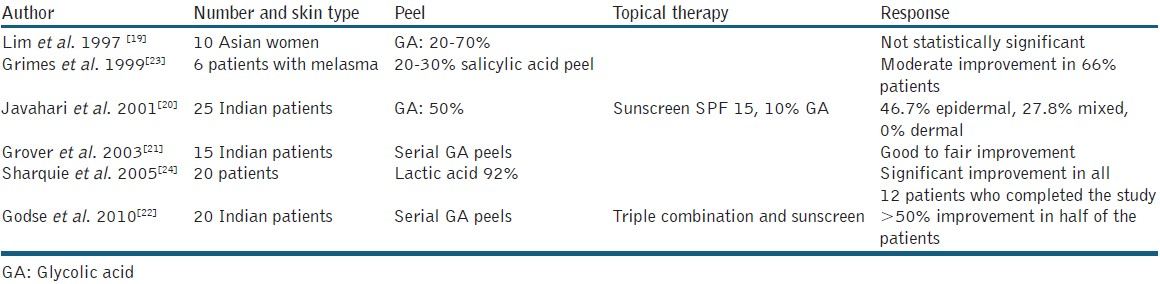
Lactic acid, also an alphahydroxy acid having activities similar to GA, has surprisingly not been used extensively as a peeling agent in the treatment of melasma, although it is a non-costly and readily available agent. The first pilot study on lactic acid was done by Sharquie et al.,[24] who found it to be a safe and effective peeling agent for melasma in dark skin. In their study of 20 patients, 92% pure lactic acid was applied for a maximum of six sessions, and a significant fall in MASI (56%) was observed in all the 12 patients who completed the study. Further, lactic acid was compared with a well-established peeling agent, Jessner's solution in a split-face design, and similar improvement was seen on both the sides with no relapse at a follow-up after six months.[29] These studies justify further experimentation with lactic acid as a peeling agent for dark skin.
Alpha keto peels
One member of this group which has gained significant attention in recent years is pyruvic acid. It is so because of its diverse keratolytic, antimicrobial and sebostatic properties as well as the ability to stimulate the formation of new collagen and elastic fibres. Apart from being effective for acne, photodamage and superficial scarring, the agent has also shown benefit in a number of pigmentary disorders in light-skinned patients.[34] However, the intense burning associated with pyruvic acid has limited its frequent use as a peeling agent for various conditions. Recently, a study was conducted by Berardesca et al.,[35] who used a new non-erythematogenic formulation of pyruvic acid and assessed its efficacy and tolerability for the treatment of photodamage, superficial scarring and melasma. It was seen that the new preparation showed significant benefit in all the three conditions with no burning either during the peel sessions or during the post-peel period. However, as all the studies have been conducted in Fitzpatrick types II to IV, it remains to be answered if the peel would do reasonably well when used on ethnic skin.
Beta hydroxy peels
Salicylic acid, a beta-hydroxy acid though traditionally used for acne, has also been tried in pigmentary disorders like melasma. In fact, ethanol solutions of salicylic acid are excellent peeling agents for numerous conditions in dark-skinned individuals including acne, melasma and PIH. The mechanism of action of salicylic acid in decreasing pigmentation is slightly different from that of GA peels. Salicylic acid is anti-inflammatory and thus it also serves to decrease the PIH which usually follows the use of peeling agents on the skin. In addition, it has a diffuse whitening effect on the skin as shown in a study by Ahn and Kim.[36] In a pilot study by Grimes et al.[23] on dark-skinned individuals, 20-30% salicylic acid peel was used to treat acne, PIH and melasma, and it was observed that almost two-thirds of the patients with melasma showed a moderate improvement. Only mild side effects were noted in 16% patients which were transient and resolved in one to two weeks. However, as there are no comparative studies, it is difficult to comment if the agent is better or inferior to the traditional glycolic peels.
Recently, a new deriveative of salicylic acid has been introduced with an additional fatty chain, the lipohydroxyacid.[37] It has increased lipophilicity compared to salicylic acid, a more targeted mechanism of action and greater keratolytic effect. It also modifies the stratum corneum making it thinner, flexible, and resistant to wrinkling and cracking. Though the peel has shown good results in patients with acne,[38] it is yet to be demonstrated if the peel is equally effective and safer than the conventional salicylic peels in patients with melasma too.
Salicylic mandelic acid peels
This novel combination of an alpha hydroxy acid with a betahydroxy acid has not been extensively tried as a peeling agent yet. Mandelic acid is one of the largest alpha hydroxy acids which penetrates the epidermis slowly and uniformly, making it an ideal peeling agent for sensitive skins.[39] Salicylic acid penetrates the skin quickly, and provides an additional benefit of decreasing the PIH. Thus, the combination of these two agents would serve as an effective peeling agent especially for ethnic skin. In our own experience, the combination does really well for various skin conditions like acne, postacne scarring and pigment dyschromias including melasma. Although there is no published data on melasma, the salicylic mandelic peels (SMPs) proved to be more efficacious for both active acne as well as post-acne hyperpigmentation as compared to the traditional GA peels.[40] The side effects were also lesser with the SMPs.
Trichloroacetic acid peel
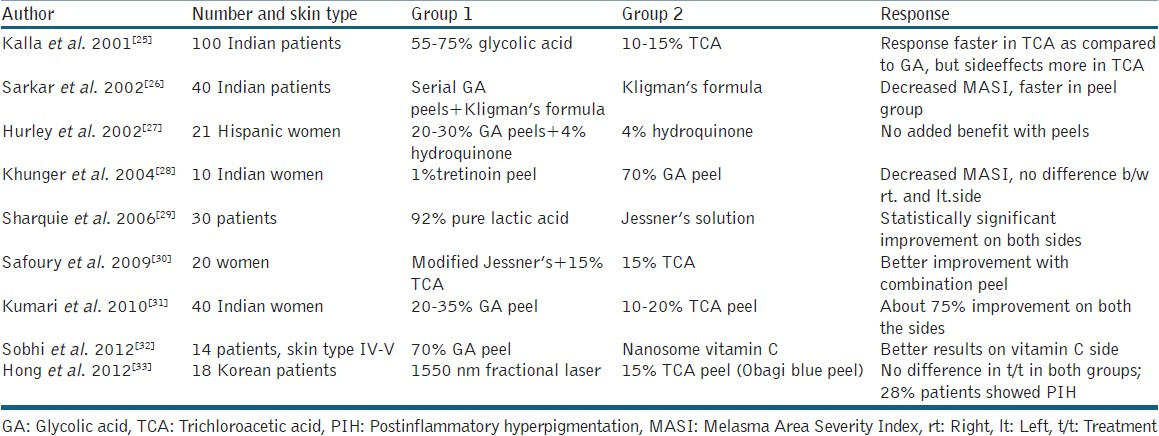
Although a commonly used peel in lighter skin, trichloroacetic acid (TCA) peel is less frequently preferred in darker skin types due to the risk of scarring and post-peel dyschromias. This is probably because frosting, the end point for a TCA peel, is not well appreciated in darker skin, and hence can lead to overtreatment. When used, only a low concentration of TCA (10-35%) is preferred which reaches upto the upper papillary dermis, and hence TCA peels are not appropriate for treating dermal and mixed forms of melasma.[41] In a comparative study on 40 Indian women by Kumari et al.,[31] the overall fall in MASI after six TCA peels was comparable to that observed with a similar number of 10-35% GA peels. However, the TCA group complained of more severe burning as compared to GA; post-peel crackening was seen in 35% patients in the TCA group and none in the GA group. To conclude, though TCA peels may be as effective as GA peels for the treatment of pigment dyschromias, caution needs to be exercised while using them in dark skin owing to a higher frequency of adverse effects.
Jessner's solution
This combination of resorcinol, salicylic acid and lactic acid in ethanol has been extensively utilised as a superficial peeling agent for all skin types. A recent interest in Jessner's solution is as a combination medium-depth peel along with other peeling agents like GA and TCA peel. Gary Monheit first popularised the combination peel using the classic Jessner's solution combined with 35% TCA.[42] Combining Jessner's solution with TCA allows a more uniform penetration and an excellent peel with a low, safe concentration of TCA. In a study of 20 female patients with melasma by Safoury et al.,[30] a combination of modified Jessner's solution with 15% TCA was compared with only 15% TCA, and it was found that the result was better on the side of the combination peel.
Tretinoin peels
Inspite of extensive use of topical tretinoin cream both alone and as a part of Kligman's formula for treating melasma, there is still a paucity of literature on the peel formulation of the agent which has shown favourable results in a few of the recent studies. The mechanism of action of tretinoin peels is proposed to be similar to that of topical tretinoin, that is, via changes in the epidermis and dispersion of melanin. The first successful use of tretinoin peel for melasma was done by Cuce et al.[43] in fair-skined patients. Following this, a pilot study was carried out in dark-skinned patients by Khunger et al.,[28] who compared 1% tretinoin peel with a standard 70 % GA peel. Ten female patients of melasma were taken up for an open left–right comparison study of 12 weeks. One percent tretinoin peel was applied on one-half of the face, whereas 70% GA was applied on the other at weekly intervals. The fall in MASI at 6 and 12 weeks with tretinoin peel was similar to that achieved with the standard glycolic solution, with only minimal side effects.
Newer peels
Despite the continued popularity of the traditional peeling agents, a number of newer peeling agents are being explored for various pigmentary dyschromias including melasma. One agent which deserves mention is the phytic acid peel. An important drawback associated with the application of alpha hydroxyl peels on the skin is the need for neutralisation and defining the exact time of neutralisation. If the peel is neutralised too quickly, it fails to produce the desired effects; whereas, if the neutralisation is delayed, it might lead to unwanted sideeffects. An easy solution to this problem is the phytic peel. It is an alpha hydroxy peel with a low pH for efficiency; it also does not need neutralisation, and therefore the danger of overpeeling is avoided.[44] The peel allows progressive and sequential actuation of its acid in a non-aggressive manner. Hence, the typical burning sensation seen with the glycolic peel is not observed with the phytic acid peels. The peel solution is left on the face until the following morning, unlike the traditional alphahydroxy peels which require immediate neutralisation. Generally, phytic acid peels are applied once a week but can be repeated twice a week when a more stimulative effect is required. Five to six peel sessions are required to achieve lightening. Although there are no published studies with the agent, in our experience the phytic peel is a very safe and effective agent for treating melasma in dark skin, and definitely needs further evaluation.
Another agent is the Obagi blue peel. It is composed of a fixed concentration of TCA with the blue peel base (containing glycerine, saponins and a nonionic blue colour base). A reduction in the surface tension of TCA, water and glycerine occurs which ensures a slow and more uniform penetration of TCA.[45] In a study of 18 Korean women, the Obagi blue peel was compared with a single sitting of 1550 nm erbiumfibre laser, and significant improvement was observed in the melasma lesions after four weeks of therapy with no difference between the laser- and peel-treated sides.[33]
A recent addition to the list of chemical peels is the amino fruit acid peels. They are potent antioxidants, and have been found to be effective as anti-ageing cosmeceuticals and act against photopigmentation.[46] In a recent study on light-skinned patients, the amino fruit acid peels were found to be as effective as the GA peels and better tolerated.[47] However, there are no studies on dark-skinned patients to substantiate this finding.
THE ROLE OF PRIMING AGENTS
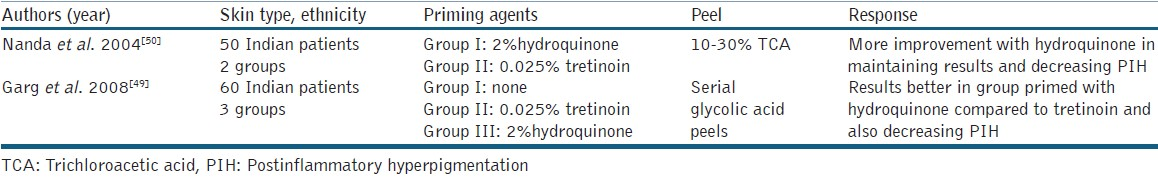
As already discussed, the biggest drawback with the use of chemical peels for melasma in ethnic skin is PIH which can either occur between the treatment sessions or after stopping treatment. Various measures have been suggested to address this problem like the concomitant use of depigmenting agents, maintenance chemical peels, photoprotection and so on. Priming or preparing the skin prior to the peel is an useful adjunctive measure which also enhances the effect of the peeling agent apart from decreasing the PIH. It involves the application of a topical depigmenting agent like hydroquinone, tretinoin or GAtwo weeks prior to the planned day of peel. Priming ensures uniform penetration of the peeling agent, enhances healing and maintains the effects achieved with the chemical peel.[48] Studies have been conducted to assess the benefit of priming agents as adjuncts to chemical peels [Table 4]. In a study by Garg et al.,[49] 60 Indian patients with melasma were randomly allocated into three groups, receiving only glycolic peel, GA primed with 0.025% tretinoin and 2% hydroquinone, respectively. The fall in MASI was highest in the group receiving 2% hydroquinone as a priming agent with minimum relapse and PIH. In another study by Nanda et al.,[50] better improvement was seen with 2% hydroquinone as a priming agent as compared to 0.025% tretinoin when used as an adjunct with 10-30% TCA peels.
HOW CAN RELAPSE BE PREVENTED?
Another problem associated with the treatment of melasma in ethnic skin is the high incidence of recurrence or relapse. This is particularly so with the use of chemical peels because they work by the temporary removal of cutaneous melanin without any action on the process of melanogenesis or melanocytes. Thus, a reasonable therapeutic approach would be to use multiple sessions of chemical peels (usually about 5-6) at a two- to four-week interval along with additional maintenance therapy with chemical peels or to use a bleaching agent (like hydroquinone, kojic acid, tretinoin) which would suppress further production of melanin.
SUMMARY
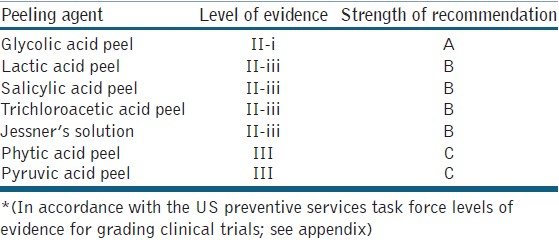
To conclude, chemical peeling proves to be a promising modality for the treatment of melasma indark-skinned patients though it is only a second-line agent or an adjunct to topical therapies. Inspite of the increasing number of new peels coming up each day, there is little published evidence supporting their use in day-to -day practice. The current levels of evidence and the strength of recommendations in accordance with the US preventive services task force levels of evidence for grading clinical trials [Appendix] for various peeling agents for dark skin is summarised in Table 5. The traditional glycolic peels prove to be the best both in terms of safety as well as efficacy. Lactic acid peels being relatively inexpensive and having shown equally good results in a few studies definitely need further experimentation. Easy phytic solution, a commonly used agent in our setup might as well replace the conventional alpha hydroxy acids because of its unique properties, whereas the TCA peels still need to be used with caution in dark skin owing to the risk of pigment dyschromias. The choice of peeling agent, the peel concentration as well as the frequency and duration of peels are all important to achieve optimum results. A few other points which deserve special attention in dark skin is the advice regarding photoprotection, the use of priming agents and the need for maintenance peels. Although the treatment of melasma in dark skin is both frustrating and challenging, cautious and judicious use of chemical peels with a few precautions offers great satisfaction both to the patient as well as the treating physician.
![US preventive services task force levels of evidence for grading clinical trials[51]](/content/173/2012/5/4/img/JCAS-5-247-g005.png)
- US preventive services task force levels of evidence for grading clinical trials[51]
Source of Support: Nil.
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
REFERENCES
- Advances in the Treatment of Melasma: A Review of the Recent Literature. Dermatol Surg. 2012;38:971-84.
- [Google Scholar]
- Association of melasma with thyroid autoimmunity and other thyroidal abnormalities and their relationship to the origin of the melasma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985;61:28-31.
- [Google Scholar]
- Prevalence and awareness of melasma during pregnancy. Int J Dermatol. 2006;45:285-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Melasma: Histopathological characteristics in 56 Korean patients. Br J Dermatol. 2002;146:228-37.
- [Google Scholar]
- Melasma of the arms associated with hormone replacement therapy. Br J Dermatol. 1999;141:592.
- [Google Scholar]
- Melasma: A clinical, light microscopic, ultrastructural, and immunofluorescence study. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1981;4:698-710.
- [Google Scholar]
- Light microscopic, immunohistochemical, and ultrastructural alterations in patients with melasma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2005;27:96-101.
- [Google Scholar]
- Different therapeutic modalities for treatment of melasma. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2009;8:275-81.
- [Google Scholar]
- The Asian dermatologic patient: Review of common pigmentary disorders and cutaneous diseases. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2009;10:153-68.
- [Google Scholar]
- Standard guidelines of care for chemical peels. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2008;74:5-12.
- [Google Scholar]
- Glycolic acid peels in the treatment of melasma among Asian women. Dermatol Surg. 1997;23:177-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- Safety and efficacy of glycolic acid facial peel in Indian women with melasma. Int J Dermatol. 2001;40:354-7.
- [Google Scholar]
- The therapeutic value of glycolic acid peels in dermatology. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2003;69:148-50.
- [Google Scholar]
- Triple combination and glycolic acid peels in melasma in Indian patients. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2011;10:68-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- The safety and efficacy of salicylic acid chemical peels in darker racial-ethnic groups. Dermatol Surg. 1999;25:18-22.
- [Google Scholar]
- Lactic acid as a new therapeutic peeling agent in melasma. Dermatol Surg. 2005;31:149-54.
- [Google Scholar]
- Chemical peeling-Glycolic acid versus trichloroacetic acid in melasma. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2001;67:82-4.
- [Google Scholar]
- The combination of glycolic acid peels with a topical regimen in the treatment of melasma in dark-skinned patients: A comparative study. Dermatol Surg. 2002;28:828-32. discussion 832
- [Google Scholar]
- Efficacy of glycolic acid peels in the treatment of melasma. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138:1578-82.
- [Google Scholar]
- Tretinoin peels versus glycolic acid peels in the treatment of Melasma in dark-skinned patients. Dermatol Surg. 2004;30:756-60. discussion 760
- [Google Scholar]
- Lactic acid chemical peels as a new therapeutic modality in melasma in comparison to Jessner's solution chemical peels. Dermatol Surg. 2006;32:1429-36.
- [Google Scholar]
- A study comparing chemicalpeeling using modified Jessner's solution and 15% trichloroacetic Acid versus 15% trichloroacetic acid in the treatment of melasma. Indian J Dermatol. 2009;54:41-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- Comparative study of trichloroacetic acid versus glycolic acid chemical peels in the treatment of melasma. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2010;76:447.
- [Google Scholar]
- A single-blinded comparative study between the use of glycolic acid 70% peel and the use of topical nanosome vitamin C iontophoresis in the treatment of melasma. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2012;11:65-71.
- [Google Scholar]
- Split-face comparative study of 1550 nm fractional photothermolysis and trichloroacetic acid 15% chemical peeling for facial melasma in Asian skin. J Cosmet Laser Ther. 2012;14:81-6.
- [Google Scholar]
- The use of pyruvic acid as a chemical peeling agent. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1989;15:13.
- [Google Scholar]
- Clinicaland Instrumental Evaluation of Skin Improvement after Treatment with a New 50% Pyruvic Acid Peel. Dermatol Surg. 2006;32:526-31.
- [Google Scholar]
- Whitening effect of salicylic acid peels in Asian patients. Dermatol Surg. 2006;32:372-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- Evidence and Considerations in the Application of Chemical Peels in Skin Disorders and Aesthetic Resurfacing. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2010;3:32-43.
- [Google Scholar]
- Comedolysis by a lipohydroxyacid formulation in acne-prone subjects. Eur J Dermatol. 2003;13:65-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Summary of mandelic acid for the improvement of skin conditions. Cosmet Dermatol. 1999;12:26-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Glycolic acidpeels versus salicylic-mandelicacid peels in active acne vulgaris and post-acne scarring and hyperpigmentation: A comparative study. Dermatol Surg. 2009;35:59-65.
- [Google Scholar]
- The Jessner's + TCA peel: A medium-depth chemical peel. J Dermatol Surg Oncol. 1989;15:945-50.
- [Google Scholar]
- Easy Phytic Solution: A New Alpha Hydroxy Acid Peel with Slow Release and without Neutralization. Int J Cosm Surg Aesth Derm. 2003;5:45-51.
- [Google Scholar]
- TCA-based bluepeel: A standardized procedure with depth control. Dermatol Surg. 1999;25:773-80.
- [Google Scholar]
- Glycolic Acid Peels Versus Amino Fruit Acid Peels in the Treatment of Melasma. Dermatol Surg. 2010;36:490-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- Manual of chemical peels. In: Superficial and medium depth. Philadelphia: Lippincott; 1995. p. :17-25.
- [Google Scholar]
- Comparative Evaluation of Beneficiary Effects of Priming Agents (2% Hydroquinone and 0.025% Retinoic Acid) in the Treatment of Melasma with Glycolic Acid Peels. Dermatol Surg. 2008;34:1032-40.
- [Google Scholar]
- Efficacy of hydroquinone (2%) versus tretinoin (0.025%) as adjunct topical agents for chemical peeling in patients of melasma. Dermatol Surg. 2004;30:385-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Guidelines for topical photodynamic therapy: Update. Br J Dermatol. 2008;159:1245-66.
- [Google Scholar]






