Translate this page into:
Aesthetic Management of Gum Hyperpigmentation by a Simple Technique
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This article was originally published by Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Dear Editor,
An attractive smile is a prerequisite for an aesthetic face. Garguilo described various components of the periodontium, giving mean dimensions of 1.07 mm for the connective tissue, 0.97 mm for the epithelial attachment and 0.69 mm for the sulcus depth.[1] Crown lengthening is a periodontal resective procedure aimed at removing supporting periodontal structures to gain sound tooth structure above the alveolar crest level. Gingivoplasty corrects the remaining thick and un-naturally shaped gingival tissue left after the gingivectomy procedure and exposes the hidden teeth.[2] Here, we present a case of aesthetic periodontal therapy to enhance the smile of the patient undergoing orthodontic treatment.
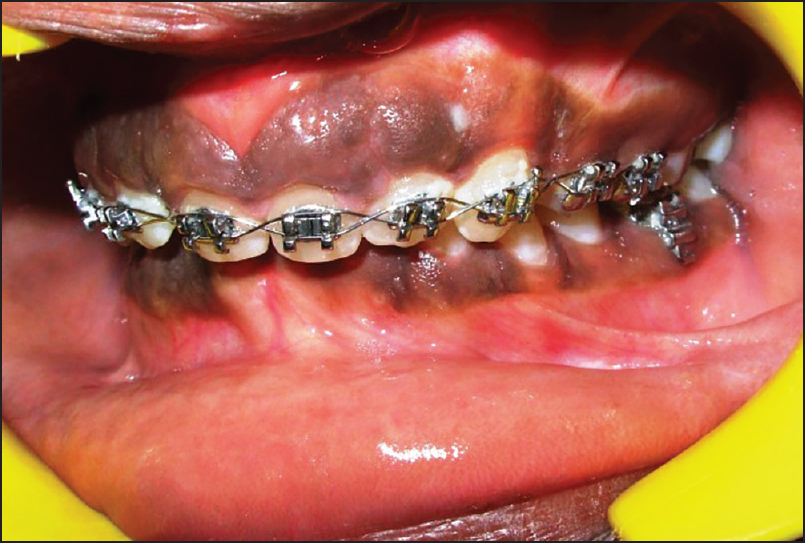
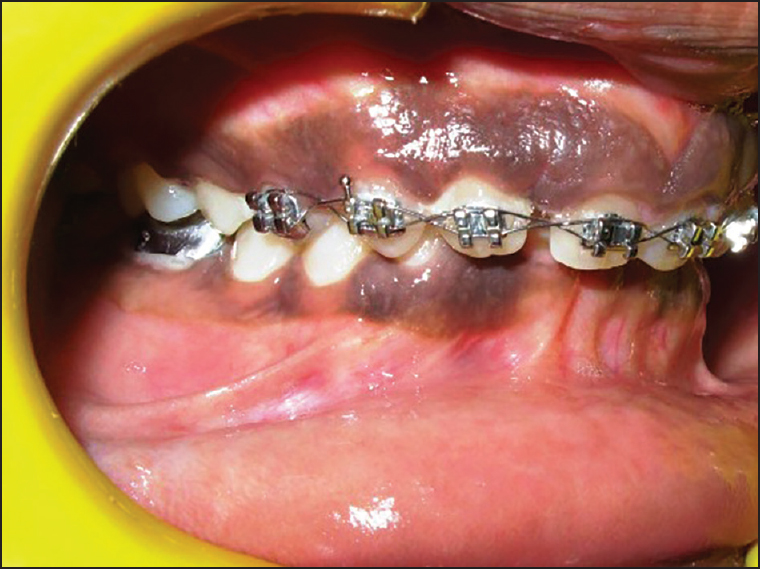
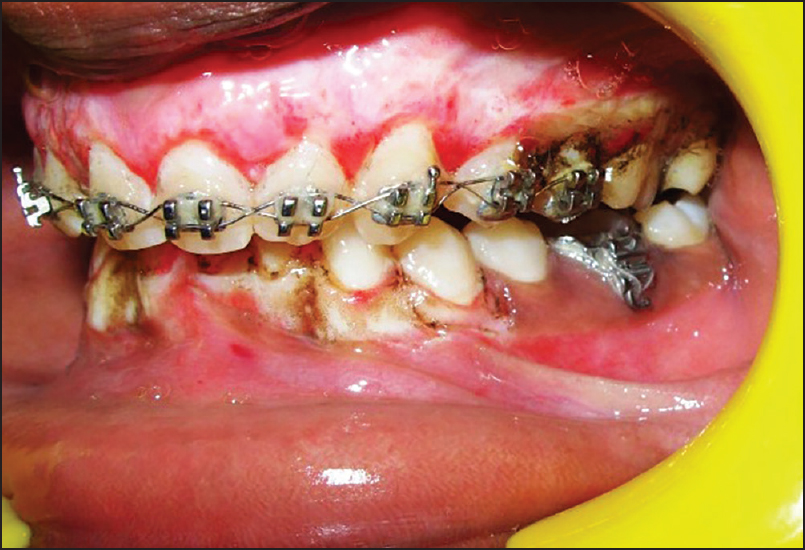
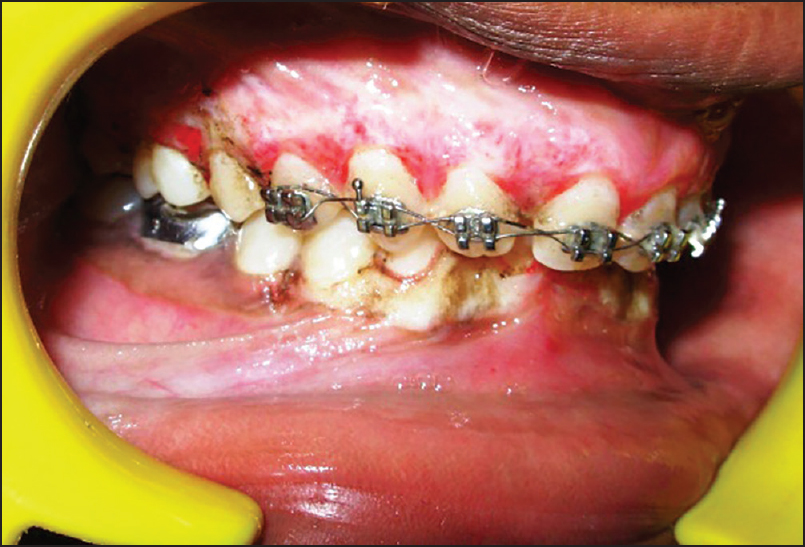
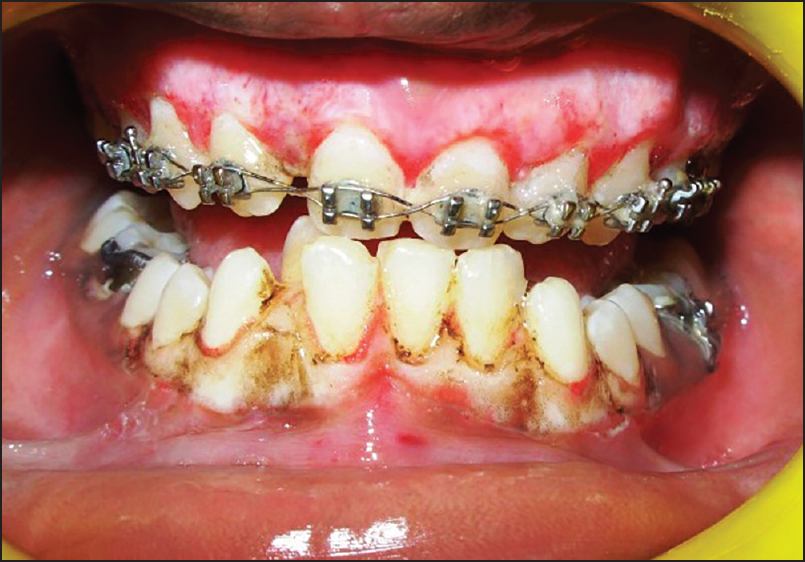
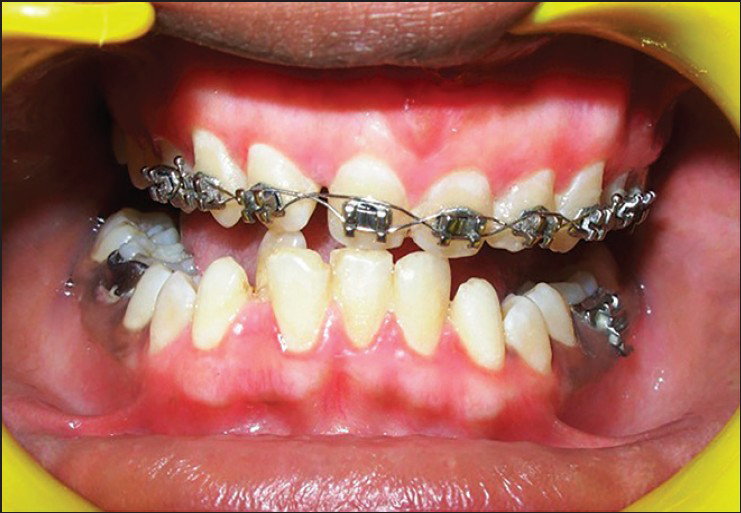
A 14-year-old male patient reported to the Department of Periodontology, referred from the department of Orthodontics, Subharti Dental College and Hospital, Meerut, Uttar Pradesh with the chief complaint of swelling of the gums in the upper teeth region and hyperpigmentation. There was no relevant medical, dental or family history. Intraoral examination revealed orthodontic molar bands and brackets on all maxillary teeth. Oral hygiene was poor, marginal and papillary gingiva appeared red and enlarged in the maxillary arch. There was increased melanin pigmentation in both arches [Figures 1–3]. The patient was informed about the treatment plan and written consent was obtained before the surgical procedures. The initial periodontal therapy comprising of scaling and root planing was performed and the patient was recalled after 1 week. Crown lengthening and depigmentation were performed under local anesthesia on the upper anterior sextant, followed by gingivoplasty. Soft tissue removal for crown-lengthening procedure was done and pigmented epithelium was removed by electrosurgery by sweeping movements of electrode tip. Periodontal dressing (Coe-pack) was placed on the surgical wound [Figure 4]. Patient was recalled after 1 week [Figure 5]. Same procedures were performed on both the sides of maxillary arch and also depigmentation was done on lower anterior teeth during the same visit [Figures 6–8]. Chlorhexidine mouthwash was prescribed twice a day daily for 3 weeks. Amoxicillin and paracetamol were given three times a day for 5 days. Patient was recalled after 2 weeks [Figures 9–11], 3 months [Figure 12] and 4 months [Figure 13] for regular follow-up.

- Pre-operative intraoral clinical photograph (frontal view)
- Pre-operative intraoral clinical photograph (left buccal view)
- Pre-operative intraoral clinical photograph (right buccal view)
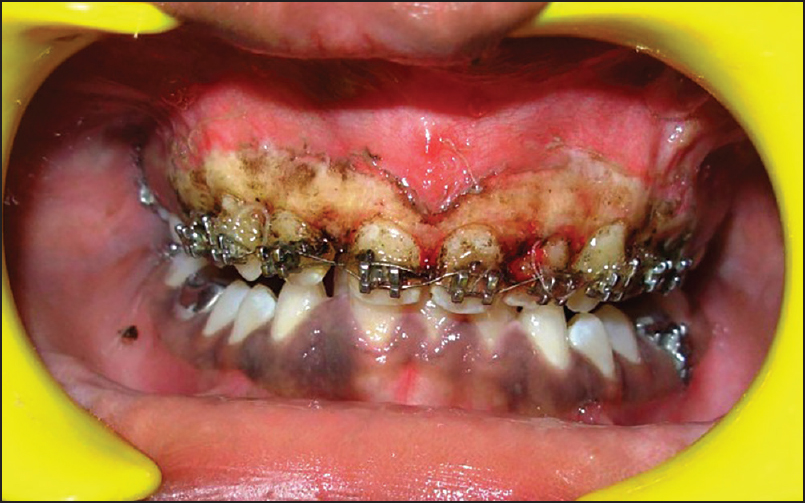
- Immediate photograph after crown lengthening, gingivoplasty and depigmentation
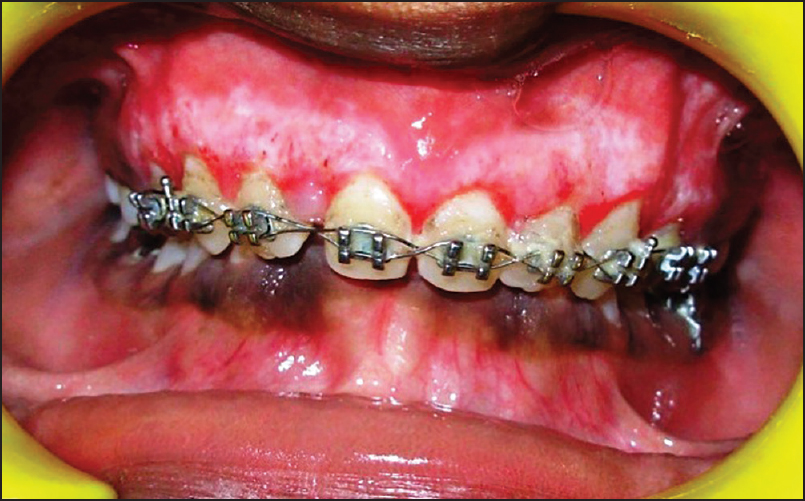
- Healing after 1 week
- Immediate post-operative photograph after same procedures on left upper posterior teeth
- Immediate post-operative photograph after same procedures on right upper posterior teeth
- Immediate post-operative photograph after depigmentation in lower arch
- Healing after 2 weeks (frontal view)
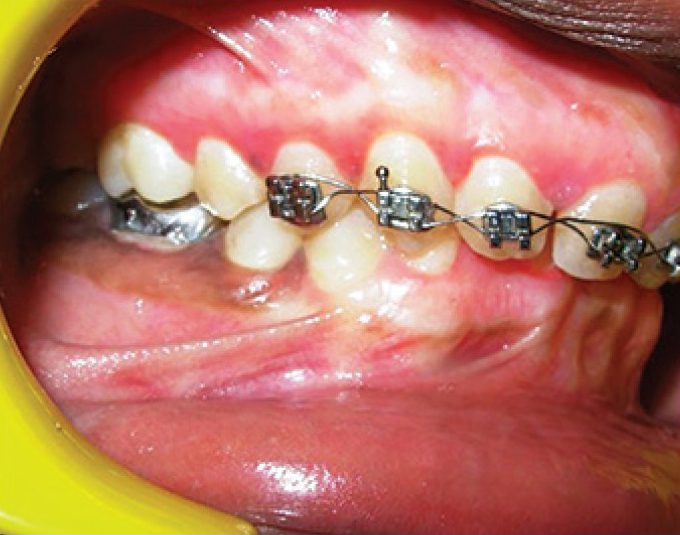
- Healing after 2 weeks (left buccal view)
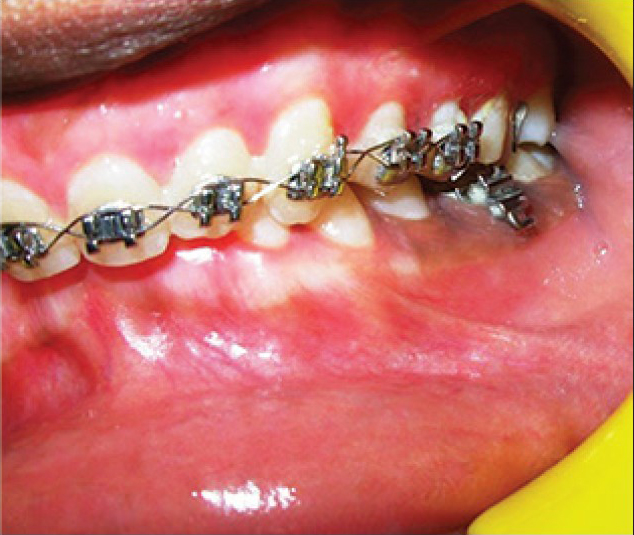
- Healing after 2 weeks (right buccal view)
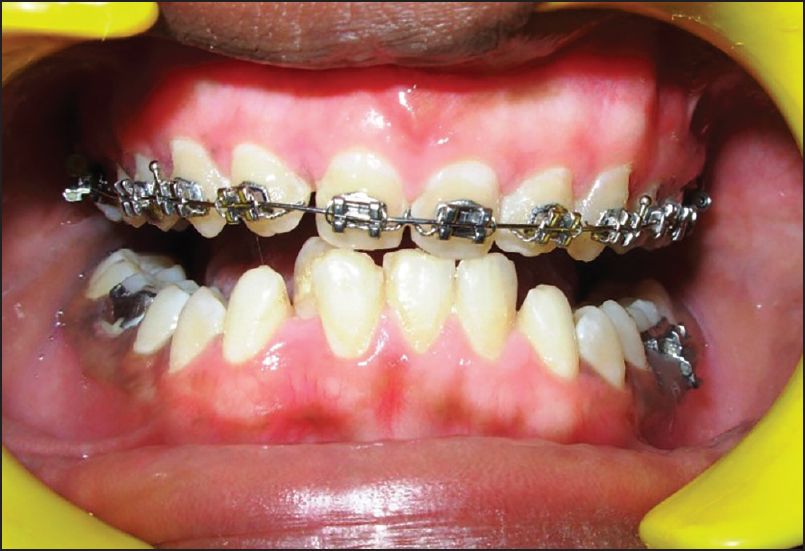
- Post-operative photograph after 3 months
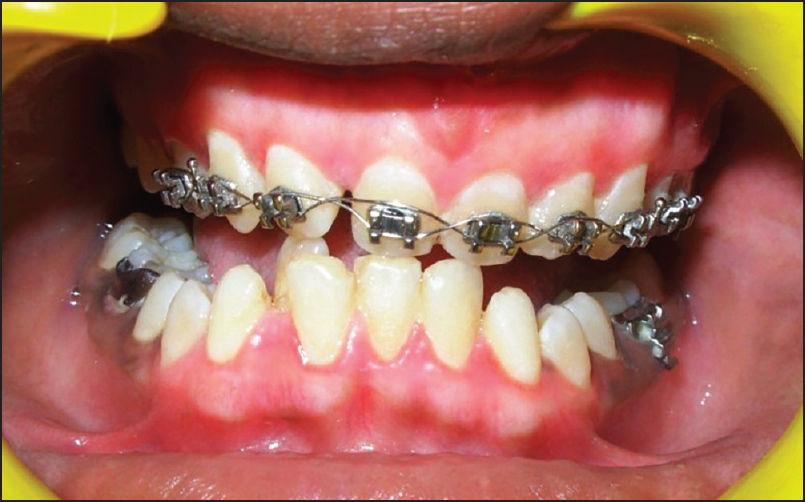
- Post-operative photograph after 4 months
The present case report describes a comprehensive interdisciplinary approach to improve smile line together with periodontal plastic surgery. The treatment results showed stability over time and a pleasant smile was achieved. It has been shown that 3 mm between the preparation margin and alveolar bone maintains periodontal health for 4-6 months.[3] This 3 mm constitutes for 1 mm supracrestal connective tissue attachment, 1 mm junctional epithelium and 1 mm for gingival sulcus on an average. This allows for adequate biologic width even when the restoration margins are placed 0.5 mm within the gingival sulcus.[4]
Selection of a technique for depigmentation of the gingiva should be based on clinical experience, patient's affordability and individual preferences. Although scalpel surgical technique for depigmentation is highly recommended being, cost effective with a faster healing period, its limitations include bleeding during the procedure and pain and discomfort after the procedure. Semiconductor diode laser 800 to 980-nm wavelength is highly absorbed by hemoglobin and other pigments as compared to other lasers.[5] Electrosurgery is a viable alternative as it is cost effective as compared to a laser. Regular maintenance visits, patient co-operation and motivation are important for improved success of interdisciplinary procedures to maintain an aesthetic smile health.
REFERENCES
- Dimensions and relationships of the dentogingival junction in humans. J Periodontol. 1961;32:261-7.
- [Google Scholar]
- Electrosurgery in aesthetic and restorative dentistry: A literature review and case reports. J Conserv Dent. 2009;12:139-44.
- [Google Scholar]
- Periodontal and prosthetic aspect of biological width part I: Violation of biologic width. Acta Stomatol Croat. 2000;34:195-7.
- [Google Scholar]
- Crown lengthening revisited. Compend Contin Educ Dent. 1999;20:527-32. 534, 536-8 passim; quiz 542
- [Google Scholar]
- Gingival depigmentation by scalpel, diode laser and electrosurgery. A Case report. Ind J dent sci. 2013;5:62-4.
- [Google Scholar]





