Translate this page into:
The Impact of Post-Acne Scars on the Quality of Life Among Young Adults in Singapore
Address for correspondence: Dr. Sai Yee Chuah, National Skin Centre, 1 Mandalay Road, Singapore - 308205. E-mail: sychuah@nsc.gov.sg
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike 3.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non commercially, as long as the author is credited and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
This article was originally published by Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Abstract
Background and Objectives:
Post-acne scarring is a common and well-known sequelae of acne vulgaris. We aim to study the impact of post-acne scarring on the quality of life (QOL) among young adults in Singapore.
Settings and Design:
This was a non-interventional prospective study.
Materials and Methods:
Patients aged 21-40 years with atrophic and hypertrophic acne scars who attended the National Skin Centre, Singapore were recruited in the study. They answered a simple questionnaire and the clinical severity of their acne scars were assessed by the doctor.
Statistical Analysis Used:
Descriptive analyses using absolute and percentage frequencies were performed on all data. The test of significance was two-sided and was set at 5% (P ≤ 0.05). Differential analyses were conducted using the parametric, independent two-sample t-test and non-parametric Mann–Whitney U-test. The statistical assessments were performed using SPSS version 18.0.
Results:
A total of 100 patients were studied. The mean patients’ subjective self-scoring on the severity of their post-acne scars was 5.78/10 and the mean Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) for post-acne scars was 5.61. Many (36%, n = 36) were self-conscious of their acne scars and 24%, (n = 24) felt that their acne scars was affecting their social activities.
Conclusions:
Our study showed that post-acne scars have a significant negative effect on the QOL of young adults. It highlights the need to increase public awareness of acne vulgaris and its sequelae through education programs and advocating early treatment to reduce the risk of scarring.
Keywords
Post-acne scars
quality of life
young adults
INTRODUCTION
Acne vulgaris is a common skin condition that starts in adolescence, with a prevalence ranging from 30% to 100%.[12] At the National Skin Centre in Singapore, acne vulgaris is the second most common skin disorder seen in its dermatology outpatient clinics.[3] This accounts for about 11% of the total number of new cases seen after eczema. Post-acne scarring is a common and well-known sequelae of acne vulgaris. Early diagnosis and management of acne vulgaris is essential in the prevention of post-acne scarring and the consequent adverse psychosocial disabilities resulting from feelings of embarrassment, frustration and poor self-esteem.
There have been few studies on the psychosocial impact of post-acne scarring in young adults and very few reports on the effects of post-acne scarring on the quality of life (QOL) in Asians. Emotional issues in these young individuals with post-acne scars need to be identified and appropriately addressed. We aim to study the impact of post-acne scarring on the QOL among young adults in Singapore.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study design
This non-interventional, prospective study was performed using a standardized questionnaire to be answered by patients who attended the outpatient clinic at the National Skin Centre, a tertiary dermatology hospital in Singapore. Patients aged 21-40 years with atrophic and hypertrophic post-acne scars were enrolled in the study after being instructed and after having granted written informed consent. Those with acne marks such as red, black or brown macular marks and those who were mentally incapable of giving consent were excluded from this study. Approval from the National Healthcare Group (NHG) Domain-Specific Review Board (DSRB), Singapore, was obtained prior to the start of the study.
Study questionnaire
The questionnaire was divided into two sections. The first section was completed by the patients. Demographics, clinical data including the type of acne lesions present during active disease (photographs with examples of comedones, papules, pustules and cysts were shown to patients to help them to recognize the features) and the average number of lesions during active acne were recorded. These information were used to assess their acne severity based on the criteria defined by Lehmann et al.,[4] i.e. mild; <20 comedones or <15 inflammatory lesions or total lesion count <30, moderate; 20-100 comedones or 15-50 inflammatory lesions or total lesion count 30-125, severe, >5 cysts or total comedone count >100 or total inflammatory count >50 or total lesion count >125. In addition, information on their acne scars and family history of acne scars or keloids (photographs of various type of acne scars were shown to patients to help them recognize features) were recorded as well.
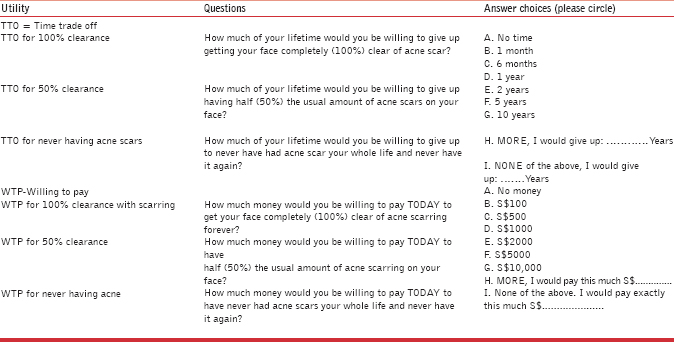
A self-acne scar severity scoring system of 0-10, with 10 being the most severe, was scored by the patients. The patient's QOL was assessed using the standard Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) questionnaires (© A Y Finlay, G K Khan April 1992 www.dermatology.org.uk) and the utility questions: Time willing to Trade off (TTO) and Willingness to Pay (WTP) (Annex 1).
The second set of the questionnaires was completed by the doctor who had assessed the patient's post-acne scars (classified as ice pick, rolling, boxcar, deep, hypertrophic or keloid) and graded into mild, moderate and severe using the qualitative global scarring grading by Goodman et al.[5678]
Statistical analysis
Descriptive analysis using absolute and percentage frequencies were performed in all data. For constant variables such as age, value (mean and median) and the scattering (SD, range) were calculated. The test of significance was two-sided and was set at 5% (P ≤ 0.05). Differential analyses were conducted using the parametric, independent two-sample t-test and non-parametric Mann–Whitney U-test. The statistical assessments were performed using SPSS version 18.0 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, USA).
RESULTS
A total of 100 patients with post-acne scars were recruited between June 2011 and September 2012. There were 57 (57%) females. The mean age was 25.6 years (SD ± 5.2 years, range 21-40 years) for females, 24.4 years (SD ± 4.2 years, range 21-36 years) for males and 25.1 years (SD ± 4.8 years, range 21-40 years) for all patients. The majority of the ethnic group was Chinese, followed by Malay, Indian and “Other” ethnicity. The ethnic distribution corresponded to the ethnic mix of the Singapore population. Most of the patients were students and Armed Forces servicemen (see Table 1 for further socio-demographic data).
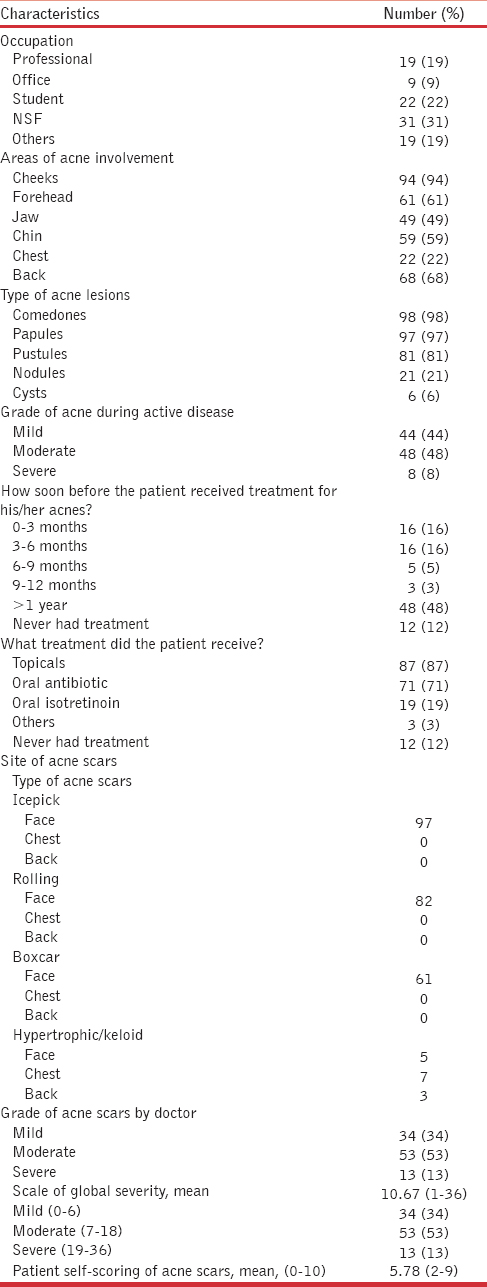
Females had an earlier onset of acne vulgaris, with the mean age of first acne vulgaris appearance at 16 years (SD ± 3.8 years, range 10-35 years), whereas the mean age of first acne vulgaris appearance was 16.7 years (SD ± 4.1 years, range 11-32 years) for men. When compared between genders, the mean duration of active acne vulgaris in females was found to be slightly longer-109.3 months (SD ± 63.7 months, range 6-300 months) than males-78.4 months (SD ± 47.7 months, range 0.5-204 months) (P < 0.05) [Table 2]. Most of these patients (48%, n = 48) had a delay of 1 year before receiving treatment for their acne vulgaris, and 12 patients (12%) never received any treatment. There was no significant difference between genders in terms of the delay of acne vulgaris treatment (P > 0.05). For those who received treatment for their acne vulgaris, most 87% had topical treatment, 71% had oral antibiotics and only 19% had oral isotretinoin.

As most acne vulgaris lesions occurred on the face, followed by the back and chest [Table 1], all patients specified that their post-acne scars were on their face (100%), followed by their back (21%) and chest (13%). The mean age of first post-acne scar presentation was 18.5 years (SD ± 4.16 years, range 12-34 years) [Table 2]. The mean duration of post-acne scars before seeking treatment in females was slightly longer, 87.5 months (SD ± 59.7 months, range 2-288 months) than males, 59.7 months (SD ± 39.9 months, range 25-204 months) (P < 0.05) [Table 2]. Majority of post-acne scars were ice pick scars 97% followed by rolling scars 82%, boxcar scars 61% and keloidal scars 15%. Fifty-one percent of the patients had at least one family member having post-acne scars, but when compared between genders, the difference was not statistically significant (P > 0.05%).
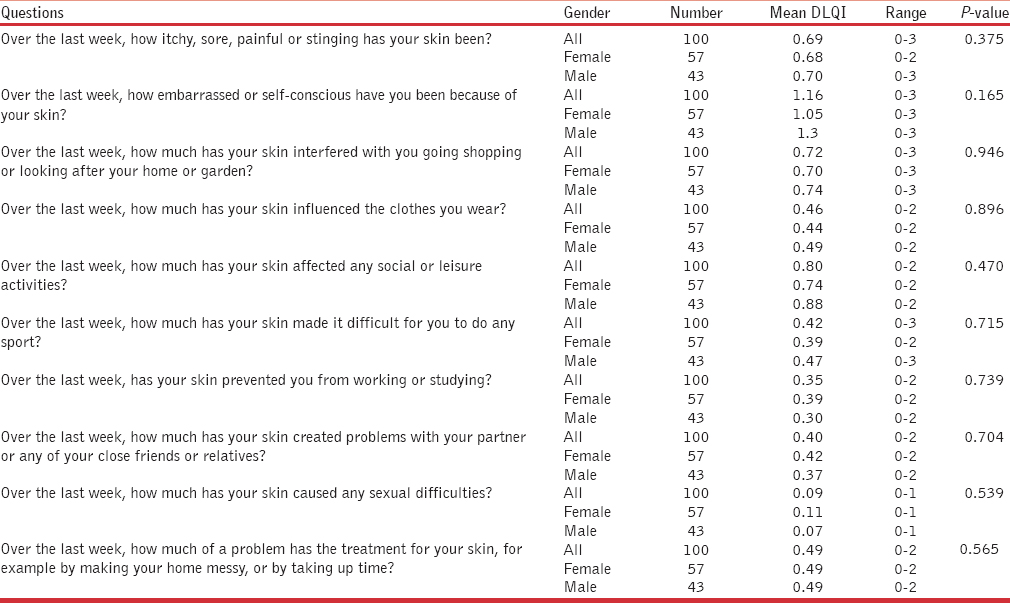
Doctors’ assessment of these patients observed that 34 patients (34%) had mild, 53 patients (53%) had moderate and 13 patients (13%) had severe post-acne scars. The mean patients’ self-scoring of the severity of their post-acne scars was 5.78/10 (SD ± 1.8, range 2-9). There was no difference in the severity scores between genders. The mean DLQI for post-acne scars was 5.61 (SD ± 4.3, range 0-17). Majority of these patients were self-conscious (36%, n = 36) and felt that their post-acne scars were affecting their social activities (24%, n = 24) [Table 3].
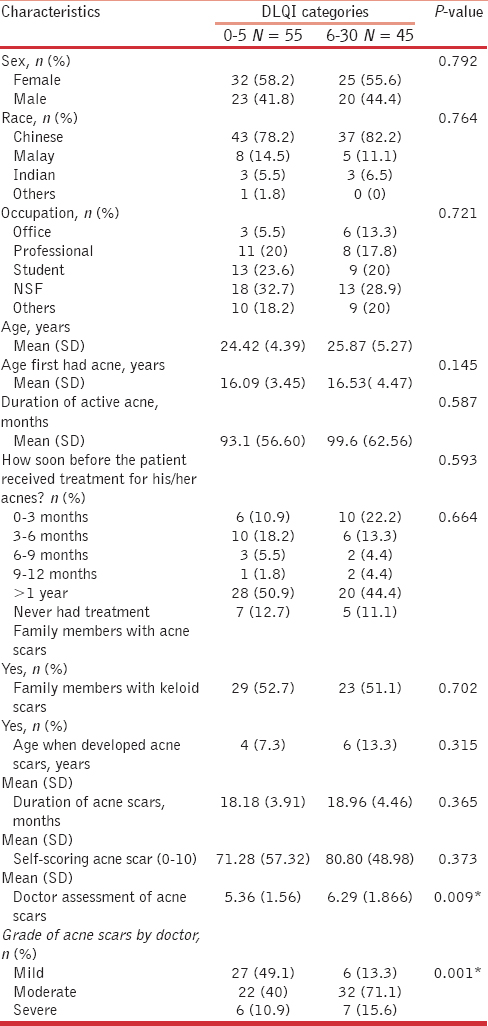
The median DLQI score was 5. In order to compare features of patients with much more severe DLQI scores with moderate DLQI scores, we divided these patients into two groups: Group 1 scoring 0-5 and group 2 scoring 6-30. Overall, the characteristics of the patients with higher DLQI score (group 2) were not statistically different from the lower DLQI score (group 1) in terms of age, sex, race, occupation, duration of active acne, family history of acne scar or keloid, age when they developed acne scar and the duration of acne scar. However, the self-scoring of post-acne scars and the doctors’ assessment of post-acne scars were statistically significant when compared between groups 1 and 2 [Table 4].
Most patients (26%) were willing to trade 1 year off their life to have 100% clear of post-acne scars, 26 (26%) patients were willing to trade 6 months off to have 50% clearance of post-acne scars and 20 (20%) patients were willing to trade 5 years off to never have any post-acne scars. Twenty-one (21%) patients were willing to pay Singapore Dollar (SGD) 2000 for 100% clearance of post-acne scars and 20 (20%) patients were willing to pay SGD 500 for 50% clearance of post-acne scars. Twenty-three (23%) patients were willing to pay SGD 5000 to never have any post-acne scars. There was no statistically significant difference between genders.
DISCUSSION
There was limited data in the literature on the QOL of patients with post-acne scars, making the comparison of the present data a challenge. Our study provided comprehensive data on the impact of post-acne scarring on the QOL among young adults in Singapore. Besides assessing the QOL using the self-acne scar severity scoring system and the DLQI, individual burden of post-acne scar was assessed using the utility questions (TTO and WTP). The potential risk factors for acne scarring were studied as well.
Acne vulgaris mainly affects adolescents and is seen in up to 80% of people aged between 11 and 30 years.[19] This was observed in our study as well, with the mean age of onset of acne vulgaris being 16.3 years. The mean duration of active acne vulgaris for all patients was 96.0 months. However, for females, it was slightly longer (109.3 months) compared with males (78.4 months) (P < 0.05) [Table 2]. In addition, we found that the mean duration of post-acne scars in females was slightly longer as well (87.5 months) when compared with males (59.7 months) (P < 0.05) [Table 2]. Although we also found that more females (n = 25) had higher DLQI scores of 6-30, this was not statistically significant (P > 0.05). These interesting findings suggested that we may need to encourage female patients to seek treatment earlier and perhaps they may need more aggressive treatment to prevent post-acne scars.
Post-acne scarring may affect up to 95% of patients with acne vulgaris and is related to severity and duration of acne vulgaris before adequate therapy.[28] Most of our patients (48%, n = 48) delayed their treatment for 1 year after the onset of their acne vulgaris and 12 patients (12%) never received any treatment. For those who received treatment for their acne vulgaris, most of them had received topical treatment (87%) and oral antibiotics (71%), and only 19 patients had oral isotretinoin (19%). Patients with acne vulgaris, based on their severity and response to treatment, are treated in accordance with an institutional guideline; mild acne vulgaris will be treated with topical treatment, moderate acne vulgaris will be treated with a combination of topical treatment and oral antibiotics and severe acne vulgaris will be treated with oral isotretinoin. Oral isotretinoin is also given to patients who have failed topical and oral antibiotics. Such data were collected and are presented in Table 1. Given that only 19% of patients were treated with oral isotretinoin, perhaps, this argues for more aggressive treatment to prevent acne scars. However, further prospective studies are required. Early and effective treatment of acne vulgaris according to various reports is the most appropriate way to prevent scarring and to minimize the psychological effects of acne vulgaris and its resultant scarring.[28] As our study patients were recruited at a tertiary referral institution, its case mix (may reflect the severity of the cases) and the nature of the study (by questionnaire survey) may lend itself to selection bias and recall bias, respectively.
In our study, the mean DLQI for post-acne scars among young adults in Singapore was 5.61. This was comparable to other debilitating skin conditions such as Behçet's syndrome (DLQI 5.7), Darier's disease (DLQI 5.89), Hailey-Hailey disease (DLQI 6.06) and rosacea (DLQI 6.1).[10] However, the DLQI score of a Thai acne study was much higher; 8.95.[11] This may be due to the fact that the Thai study was a combined assessment of acne vulgaris and acne scars rather than acne scars alone. Majority of our patients were affected by DLQI questions two, five and nine, i.e. they were self-conscious (36%), felt that their post-acne scars was affecting their social activities (24%) and interfered with them going out or shopping (18%). The lowest mean DLQI score was on question nine, which asked about sexual difficulties (score 0.09) [Table 3]. This was probably a feature of the Asian culture, where they seem to be embarrassed when asked about personal relationships. This was a similar finding in the Thai study.[11]
When comparing the patients with moderate DLQI scores with a much more severe DLQI score (groups 1 and 2), the self-scoring of post-acne scars and the doctors’ assessments of post-acne scars were statistically significant. This indicated that the patients’ self-assessments and the doctors’ assessments were generally concordant. Most patients with mild post-acne scars (49.1%, n = 27) had low DLQI scores. However, some patients with mild post-acne scars (13.3%, n = 6) also had a high DLQI score [Table 4]. On the contrary, six patients (10.9%) with severe post-acne scars had a low DLQI score. This discordance may represent the variation in the perception of post-acne scars on the image of the patients. This may also be accounted by the subjective inter-observer variation among the doctors assessing the acne by severity scores at different clinic visits at our institution.
Many patients (26%) were willing to trade 1 year off their life and 21 patients (21%) were willing to pay SGD 2000 to have all their post-acne scars cleared. Compared with the other studies in the West, this is higher than that of rosacea (SGD 821) but lower than that of vitiligo (SGD 3284).[12] As many of our patients (53%) were young (students and national serviceman), this suggested that the post-acne scars may influence their psychological well-being and also their willingness to pay.
CONCLUSIONS
Our study showed that post-acne scars have a significant negative effect on the QOL of young adults, thereby highlighting the need to increase public awareness through education programs and early treatment to reduce the risk of post-acne scar development. Physicians should not underestimate the QOL impairment of patients with post-acne scars. The use of these simple questionnaires may help physicians recognize the presence of psychiatric distress and facilitate further management and referral to a psychologist. At a national level, this calls for greater allocation of healthcare resources in this relatively under-studied area.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The authors acknowledge Dr. Shen Liang, Senior Biostatistician, Biostatistics Unit, NUS for the statistical analysis and support.
Source of Support: Nil.
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
References
- The prevalence of common skin conditions in Australian school students: 3. acne vulgaris. Br J Dermatol. 1998;139:840-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- A clinical evaluation of acne scarring and its incidence. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1994;19:303-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Community-based study of acne vulgaris in adolescents in Singapore. Br J Dermatol. 2007;157:547-51.
- [Google Scholar]
- Postacne scarring: A qualitative global scarring grading system. Dermatol Surg. 2006;32:1458-66.
- [Google Scholar]
- Postacne scarring — a quantitative global scarring grading system. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2006;5:48-52.
- [Google Scholar]
- Acne and acne scarring — The case for active and early intervention. Aust Fam Physician. 2006;35:503-4.
- [Google Scholar]
- An update on the pathogenesis and management of acne vulgaris. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51(Suppl 1):S36-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- The dermatology life quality index 1994-2007: A comprehensive review of validation data and clinical results. Br J Dermatol. 2008;159:997-1035.
- [Google Scholar]
- Dermatology Life quality index in Thai patients with acne. Siriraj Med J. 2007;59:3-7.
- [Google Scholar]
- Willingness to pay and quality of life in patients with rosacea. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:734-8.
- [Google Scholar]






