Translate this page into:
Dermatological Research in India: A Brief Bibliometric Analysis of Publications During 1999–2019
Address for correspondence: Dr. Virendra S. Ligade, Department of Pharmacy Management, Manipal College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Manipal Academy of Higher Education, Manipal, Karnataka, India. E-mail: virendra.sl@manipal.edu
This is an open access journal, and articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 License, which allows others to remix, tweak, and build upon the work non-commercially, as long as appropriate credit is given and the new creations are licensed under the identical terms.
This article was originally published by Wolters Kluwer - Medknow and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Abstract
Abstract
Background:
Dermatology is the science of the skin. In India, dermatology came into picture in the twentieth century. Today’s dermatology practiced in India is the modern approach developed and established in western countries based on western medical theory, knowledge, experience, and results from study. Growth of dermatology field in India has progressed since two to three decades. This paper assesses the contributions made by India in the dermatology field by analyzing the total number of publications in top dermatological journals.
Materials and Methods:
SCImago Journal Rank indicator (2019) was used to search for top dermatology journals and publication metrics was recorded from respective journal websites. Simple statistics tools were used to determine the number of publications during this 20-year period.
Results:
From 1999 to 2019, there were 547 publications from India, in the top dermatologic journals. It was noted that, original research article contributes maximum number of documents (136). Journal of Dermatology had a maximum number of publications with 174 when compared to other journals. Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh’ had a maximum number of publication (150).
Conclusion:
The last 20 years have seen a massive increase in the field of dermatology. Today, dermatology is a well-developed field in India. From 1999 to 2019, there is an increase in the trend of publications along with the collaborative publications in the top dermatologic journals. This show the encouraging trend in terms of publications from India in past 20 years.
Keywords
Dermatology
India
journals
publications
INTRODUCTION
Dermatology is the science of skin and its appendages, which evolved from general internal medicine during the nineteenth century.[12] Until this time, physicians with few exceptions were little concerned with the skin. In India, dermatology came into picture in the twentieth century, even though skin infections such as chicken pox, leprosy, etc. were recognized long back. Indian dermatology deviates from contemporary dermatology practiced elsewhere.[2] From the beginning, dermatology was taught as part of the internal medicine. In 1895, the first chair of dermatology was established at Grant Government Medical College and JJ Hospital, Mumbai.[3] In the year 1935, Dr Narayan Rao published “Indian Journal of Venereal Diseases” in India, the first ever journal in this field. This was renamed as “Indian Journal of Venereal Diseases and Dermatology” in 1940; finally, in 1955, the association’s official journal was issued under the new title “Indian Journal of Dermatology and Venereology.”[4]Indian Journal of Dermatology (IJD) is another quality and reputed journal published from India.[5] A comprehensive study is lacking on the development and progress of dermatology in India.
There is no systemic as well as exhaustive study yet in the history of dermatology in this country, although the subject was recognized in the past. The glorious history of medical science including that of dermatology should be recovered and promoted in the international platform.[6] Today’s dermatology practiced in India is the modern approach developed and established in western countries based on western medical theory, knowledge, experience, and results from the study. With the advancement of research carried out, this country becomes evidence that the Indian scenario completely defers from the western scenario. Today, dermatology is a well-developed field in India. The establishment of skin department in teaching hospitals helped the country to develop the dermatology service. The last 20 years have seen a massive increase in the field of dermatology. The aim of the research was to establish a new level of understanding in this very important field of health science, enabling us to use the latest findings on the manifestations and causes of dermatological diseases. The number of research publications in quality dermatology journals mirrors the research activity within a country and international collaborative work. In this regard, assessing contribution of this field to scientific literature was the main focus of the study. The analysis was through the bibliometric study. Bibliometry is a popular and novel scientific field investigating academic literature and analyzing publication trends and patterns in a certain area.[78] In this study, we attempted to analyze the contributions of Indian scientific literature and collaborative research in the field of dermatology from the past 20 years.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The relevant data for the study were obtained through secondary data resources, available in the public domain. For selection of top dermatology journals, metrics provided by SCImago Journal (2019) were used. Our focus of the study was research output made by Indian authors and collaborative research made by Indian authors. In order to search published documents made by India, respective dermatology journal websites were explored. The keyword used for the study was “India.” Archives of published issues were analyzed from all top dermatology journals. The details and/or authors information was recorded manually in MS Word. The published documents in which Indian author collaborated with other countries were also included in the study. The study period was between January 1, 1999 and December 31, 2019. The collected data are then analyzed and recorded separately in MS Word, and MS Excel was used to organize, tabulate, and analyze the necessary data for the study. The journals selected for the study were British Journal of Dermatology, JAMA Dermatology, Journal of Investigative Dermatology, Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, American Journal of Clinical Dermatology, Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, Dermatologic Clinics, Experimental Dermatology, and Journal of Dermatological Science. These journals were selected based on their respective impact factors and total citations according to the SCImago Journal Rank indicator.[910] The data are presented in a tabular and graphical form.
Results and Discussion
Table 1 presents total document types in scientific literature related to dermatology published between 1999 and 2019. It was noted that original research article contributes maximum number of documents (136), followed by letters to the editor (104), short report (21), review article (11), research letter (11), case report (9), full length article (5), observation (2), and systematic review (1).
| Document type | Number of documents |
|---|---|
| Case report | 9 |
| Original research article | 136 |
| Correspondence | 11 |
| Letter to the editor | 104 |
| Image correspondence | 13 |
| Short report | 21 |
| Regular article | 1 |
| Clinical and laboratory investigation | 11 |
| Concise communication | 5 |
| Translational research | 5 |
| Original investigation | 5 |
| Full length article | 5 |
| Research letter | 16 |
| Review article | 11 |
| Observation | 2 |
| Short communication | 2 |
| Systematic review | 1 |
| Clinical trial | 1 |
| Guidelines | 1 |
Figure 1 illustrates the total number of published documents by Indian authors and collaborative published documents by Indian authors along with international authors. Dermatology research has grown markedly in the past two decades. From 1999 to 2019, there were 547 publications from India in the top dermatologic journals. It was noted that Indian authors published 104 articles in collaboration with the authors of different countries in the top dermatologic journals. In 1999, there was one publication from India. It was observed that year 2014 had a maximum number of publications from India with 132, followed by year 2015 with 71 publications. Further, it was noted that in 2016, maximum numbers of collaborative publications were 16; there were no publications published in the year 2000. The number of publications in these top dermatological journals in 2014 was 132, the highest ever, followed by 2015 with 71 publications.
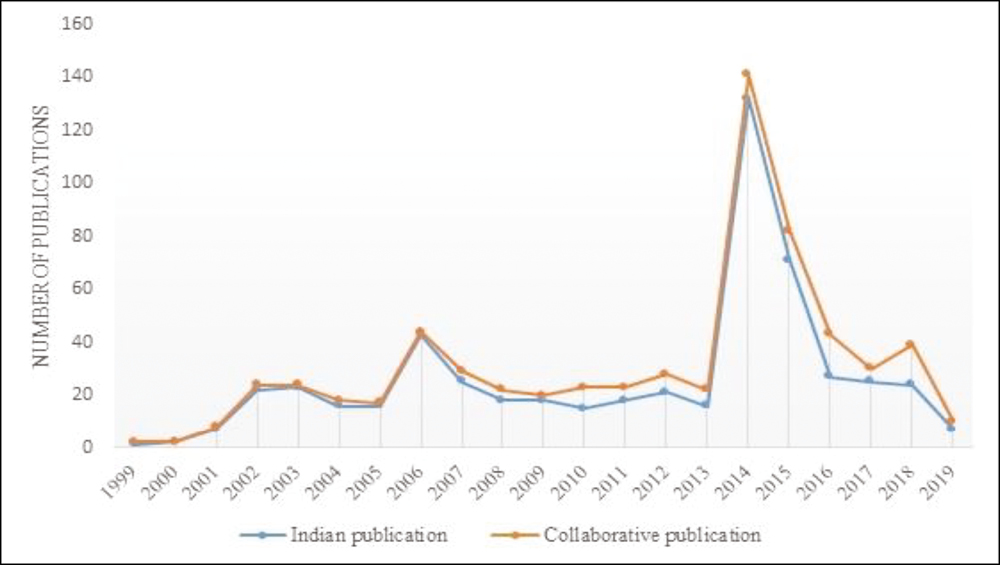
- Total number of Indian and collaborative publications from 1999 to 2019
From Table 2 and Figures 2 to 4, it is found that among the top journals, Journal of Dermatology had a maximum number of publications with 174 when compared with other journals. British Journal of Dermatology had 112, Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 170, and JAMA 47. Collaborative research publications were higher in British Journal of Dermatology (41) and Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (22). The number of publications in this top journal was 16 in 2016, the highest ever, followed by 2018, i.e. 15 publications; no publication was found in the year 2000 in this top journal.
| S. No. | Name of journals | Total Indian authored publications (1999–2019) | Total international collaborative publications (1999–2019) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | British Journal of Dermatology | 112 | 41 |
| 2 | JAMA Dermatology | 12 | 3 |
| 3 | Journal of Investigative Dermatology | 5 | 10 |
| 4 | Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology | 47 | 7 |
| 5 | American Journal of Clinical Dermatology | 5 | 2 |
| 6 | Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology | 170 | 22 |
| 7 | Dermatologic Clinics | 3 | 1 |
| 8 | Experimental Dermatology | 11 | 8 |
| 9 | Journal of Dermatological Science | 8 | 1 |
| 10 | Journal of Dermatology | 174 | 9 |
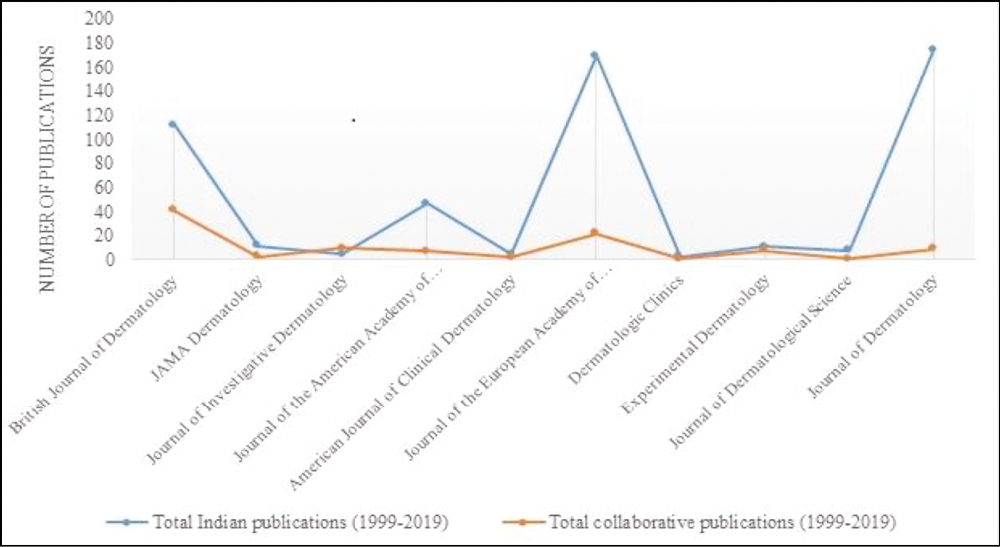
- Total number of Indian and collaborative publications in top dermatology journals
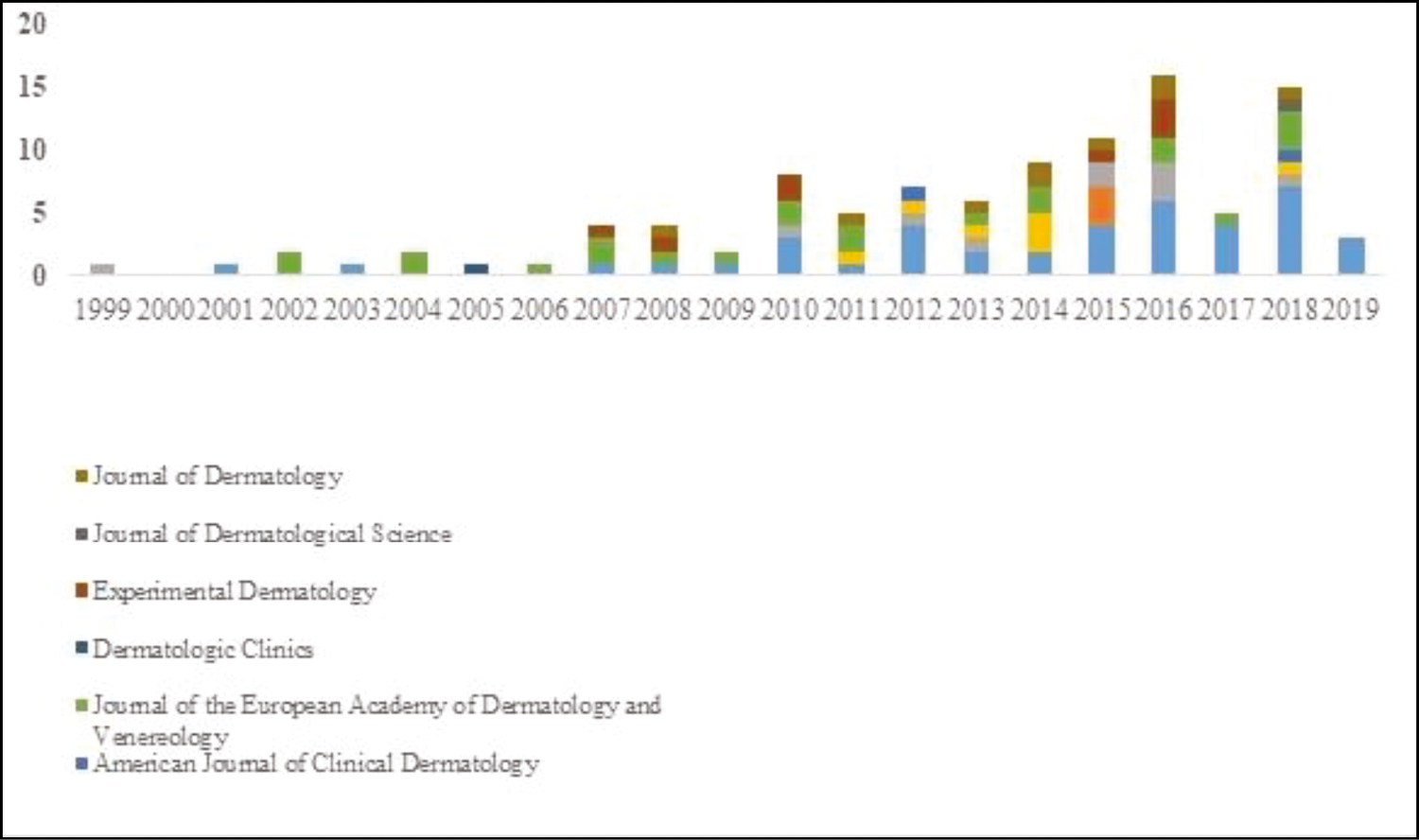
- Year-wise total number of Indian publications in top dermatology journals from 1999 to 2019
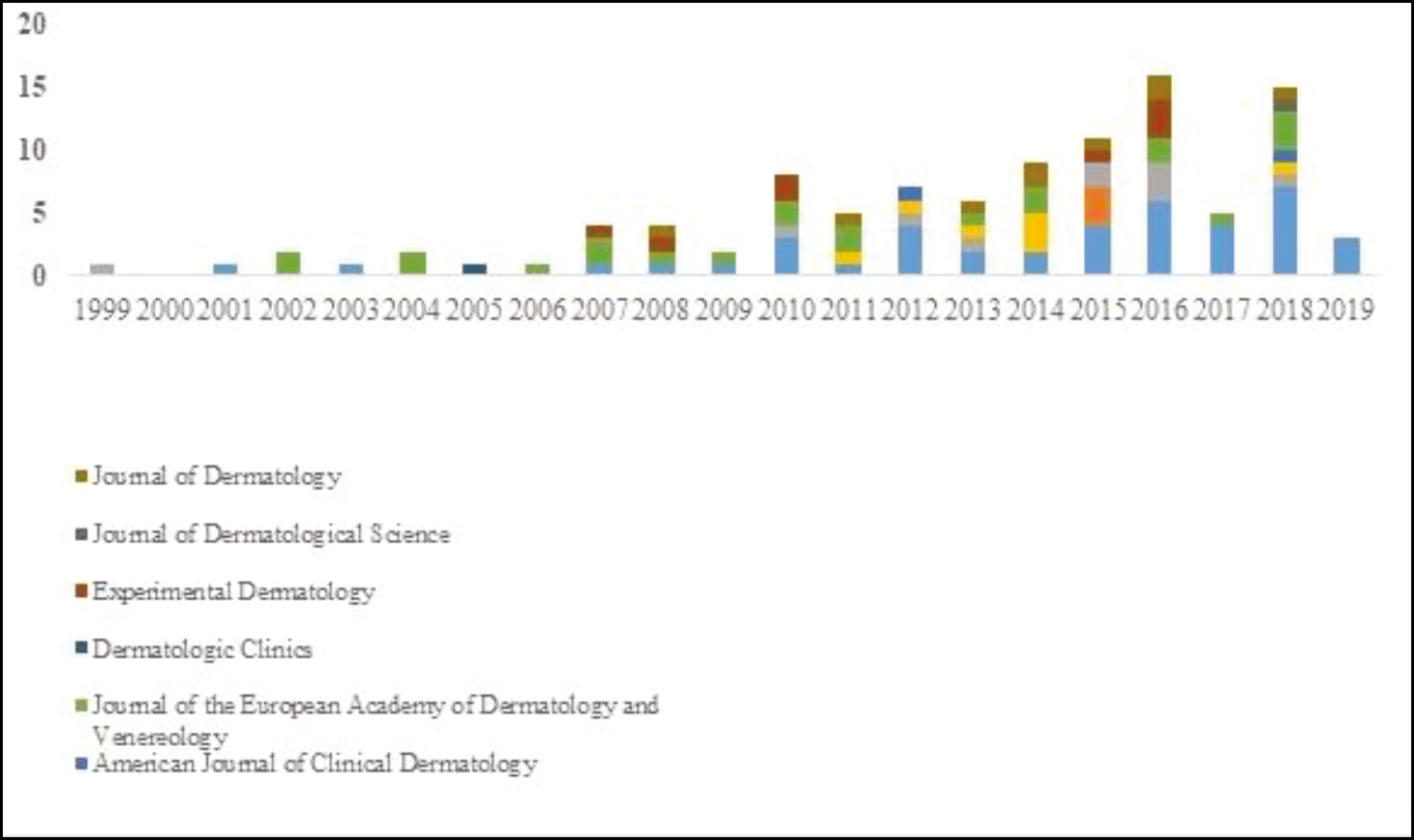
- Year-wise total number of collaborative publications in top dermatology journals from 1999 to 2019
Table 3 shows that the total number of Indian authors contributed in the top dermatologic journal was 1731. The total number of international authors’ (other country authors collaborated with Indian authors) contribution was 527.
| Number of Indian authors | 1731 |
|---|---|
| Number of international authors | 527 |
| Total number of authors | 2258 |
Table 4 shows top Indian institutions by number of publications in the literature related to dermatology. It was revealed that Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh had the maximum number of publications (150), followed by All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi (80), Maulana Azad Medical College, Delhi, India (29), Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research, Puducherry (24), Lady Harding Medical College (17), Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda, Vadodara, Gujarat (13), Government Medical College and Hospital, Chandigarh (13), Safdarjung Hospital, New Delhi (11), Christian Medical College Hospital, Vellore, Tamil Nadu (11), and Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi (6).
| S. No. | Institutes | Published documents |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh | 150 |
| 2 | All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi (AIIMS) | 80 |
| 3 | Maulana Azad Medical College, Delhi, India | 29 |
| 4 | Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research, Puducherry | 24 |
| 5 | Lady Harding Medical College | 17 |
| 6 | Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda, Vadodara, Gujarat | 13 |
| 7 | Government Medical College and Hospital, Chandigarh | 13 |
| 8 | Safdarjung Hospital, New Delhi | 11 |
| 9 | Christian Medical College Hospital, Vellore, Tamil Nadu | 11 |
| 10 | Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi | 6 |
CONCLUSION
Research is a scalable indicator of productive contribution to the knowledge continuum of dermatology field. Research collaborations among Indian dermatologists/researchers in India have increased research performance in terms of publications, which impacts overall research impact. From year 1999 to 2019, there is an increase in the trend of publications along with collaborative publications in the top dermatologic journals. There is an encouraging trend in terms of publications from India in the past 20 years. Although the contributions of Indian authors have increased in international journals over the years, input is still scarce. These findings provide a context for analyzing current research publication strengths and gaps in the current state of dermatology research. More consideration is needed to be given by the Indian dermatologists/researchers to conduct quality research and publish in international and reputed dermatological journals.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
REFERENCES
- History of dermatology, venereology and leprology in India. J Postgrad Med. 2002;48:160-5.
- [Google Scholar]
- Emergence of dermatology in India. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2009;75:86-92.
- [Google Scholar]
- History of dermatology in India till date. Shodhganga; Available from: http://hdl.handle.net/10603/48843
- [Google Scholar]
- Dermatology in India and Indian dermatology: A medico-historical perspective. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7:235-43.
- [Google Scholar]
- Bibliometric analysis on global Behçet disease publications during 1980-2014: Is there a silk road in the literature? J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017;31:518-22.
- [Google Scholar]
- History of dermatology in India till date. Doctoral dissertation. India: Gujarat University; 2007. Retrieved from http://hdl.handle.net/10603/48843
- Indian Journal of Dermatology consolidates its position in 2010. Indian J Dermatol. 2011;56:1.
- [Google Scholar]
- Global trends of botulinum toxin literature: A bibliometric analysis of botulinum toxin publications between 1975 and 2017. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2020;13:95-102.
- [Google Scholar]
- Analysing China’s contributions to major dermatologic journals from the past 20 years. Dermatol Online J. 2020;26:8.
- [Google Scholar]






