Translate this page into:
Eyelid Cutaneous Horn
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 Unported, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
This article was originally published by Medknow Publications & Media Pvt Ltd and was migrated to Scientific Scholar after the change of Publisher.
Sir,
We read with great interest the article by Oludiran et al., “Cutaneous horns in an African population”, reporting their experiences with six patients who had cutaneous horns on scalp and extremities.[1] In this article we want to present a patient with an eyelid cutaneous horn.
Cutaneous horn is a relatively rare tumor, most often arising on sun-exposed skin in elderly men.[2] The important issue is not the horn itself, which is dead keratin, but rather the underlying condition, which may be benign, premalignant, or malignant.[3] Our patient, a 78-year-old farmer, presented with a 3-year history of a slowly growing lesion on his left lower eyelid. Physical examination revealed a solitary firm horn like projection, 5 cm in height with a hyperkeratotic surface without associated lymphadenopathy [Figure 1]. The lesion was completely excised surgically. Histology was reported as well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma [Figure 2]. Investigations showed no metastases. The patient underwent two additional operations to achieve free surgical margins. On follow up, patient had an uneventful course with no clinical relapse [Figure 3].
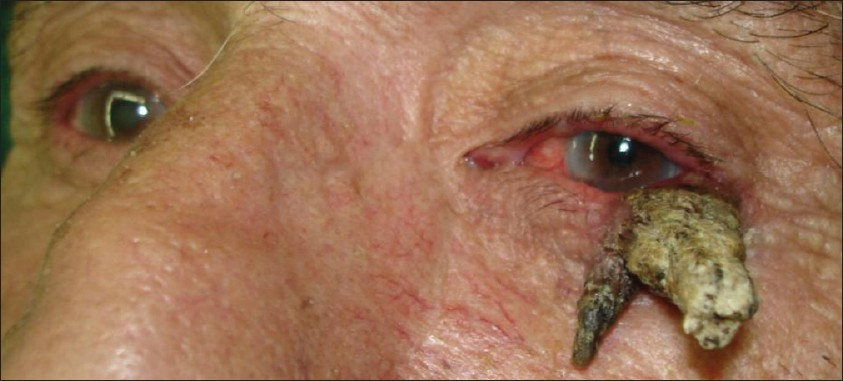
- Left lower eyelid cutaneous horn
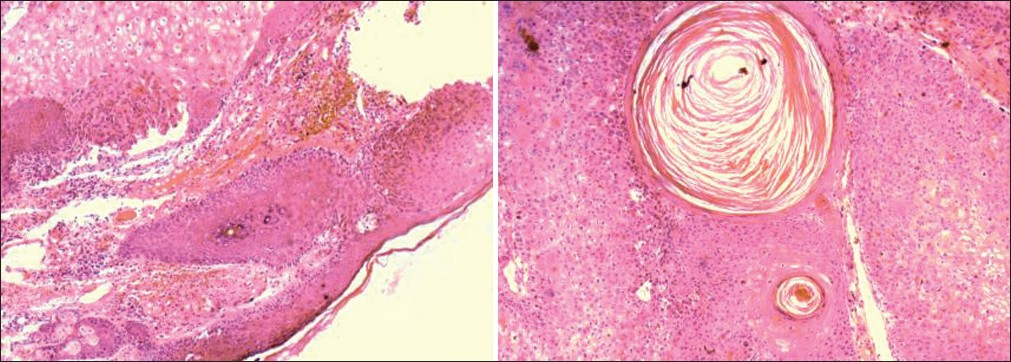
- Hematoxylin and eosin-stained sections showing well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma
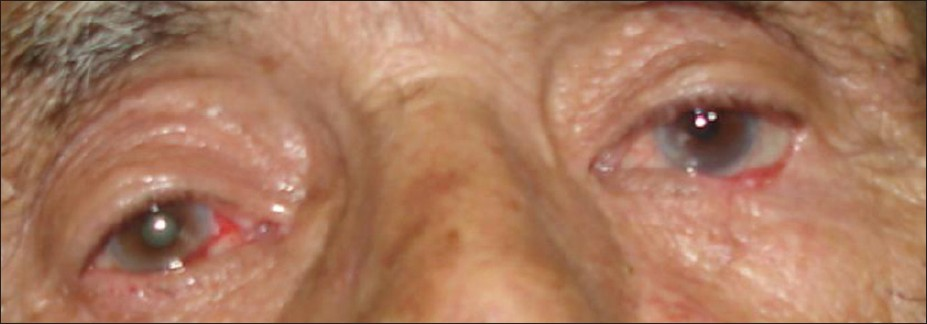
- Post-op appearance, after one year
Various types of associated lesions may be found at the base of a cutaneous horn, including viral warts, actinic keratosis, keratoacanthoma, seborrheic keratosis, pyogenic granuloma, discoid lupus erythermatosus, verruca vulgaris, Bowen's disease, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma.[4–7] In a study performed on 48 cases with eyelid horns, by Mencía-Gutiérrez et al., 23% of them were premalignant and malignant.[8] Although it is very difficult to distinguish between benign, premalignant, and malignant lesions, larger size of lesions and tenderness at base of lesions are signs in favor of malignancy. Treatment depends on the type of lesion and its malignant potential.[3] Therefore, prompt diagnosis of the underlying lesion by appropriate biopsy is mandatory. In cases of benign lesions, the biopsy may be both diagnostic and therapeutic, while for malignant tumors, complete surgical excision with appropriate margin is usually required.[3] So, in every patient with cutaneous horn, an underlying disease must be looked for.
REFERENCES
- Everard home, John hunter, and cutaneous horns: A historical review. Am J Dermatopathol. 2001;23:362-9.
- [Google Scholar]
- Giant cutaneous horn in an African woman: A case report. J Med Case Reports. 2007;1:170.
- [Google Scholar]
- Images in clinical medicine.Squamous cell carcinoma manifesting as a cutaneous horn. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:e10.
- [Google Scholar]
- Cutaneous horn arising in chronic discoid lupus erythematosus. Arch Dermatol. 1985;121:837-8.
- [Google Scholar]
- Cutaneous horns of the eyelid: A clinicopathological study of 48 cases. J Cutan Pathol. 2004;31:539-43.
- [Google Scholar]





