Translate this page into:
Hyperocclusive technique for topical anesthesia for injecting botulinum toxin in palmar hyperhidrosis
*Corresponding author: Pankaj Das, Department of Dermatology, Base Hospital Delhi Cantt and Army College of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, India. pankaj3609@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Vashisht D, Das P, Choudhary SS, Singh GK, Sinha P, Bahuguna A, et al. Hyperocclusive technique for topical anesthesia for injecting botulinum toxin in palmar hyperhidrosis. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2024;17:335-6. doi: 10.4103/JCAS.JCAS_224_22
Abstract
Injecting botulinum toxin under simple topical anesthesia using a eutectic mixture of lignocaine and prilocaine is a painful procedure. A simple hyper-occlusive modification in the existing technique of topical anesthesia of palms facilitates painless injections leading to greater patient satisfaction and compliance.
Keywords
Botulinum toxin
Hyperhidrosis
Hyperocclusion
Topical anesthesia
PROBLEM STATEMENT
Palms and soles have thick stratum corneum as well as dense nerve endings causing difficulty in achieving anesthesia. The existing technique of anesthetizing palms consists of applying lignocaineprilocaine mixture on the palmar aspect of hands for an hour or nerve blocks at wrist. Achieving anesthesia using the topical method is simple but results in suboptimal anesthesia causing significant pain while injecting botulinum toxin. Administering nerve blocks is a blind as well as a skilled procedure, which needs to be mastered to achieve optimal anesthesia and to prevent complications.
RECOMMENDED SOLUTION
We tested a hyperocclusive technique consisting of applying lignocaine-prilocaine mixture on both palms under occlusion with a latex surgical glove in two successive continuous sittings for an hour each to achieve topical anesthesia in three patients. Two pairs of latex surgical gloves were used for hands for occlusion—the inner glove being half a size larger than the patient’s hand size for easy sliding into the hands so that it does not dislodge the cream and the outer gloves being half a size smaller than patient’s hand size for better “snug- occlusion” [Figure 1]. In addition, due to occlusion, the palms achieved adequate softness facilitating easy injection into the superficial dermis [Figure 2]. None of the patients complained of any pain while injecting botulinum toxin. This technique is simple yet reliable in achieving effective anesthesia in palms. The technique is easily reproducible and does not require skills such as that of nerve blocks at wrist. The only disadvantage is the time taken for the occlusion—that is 2 hours.
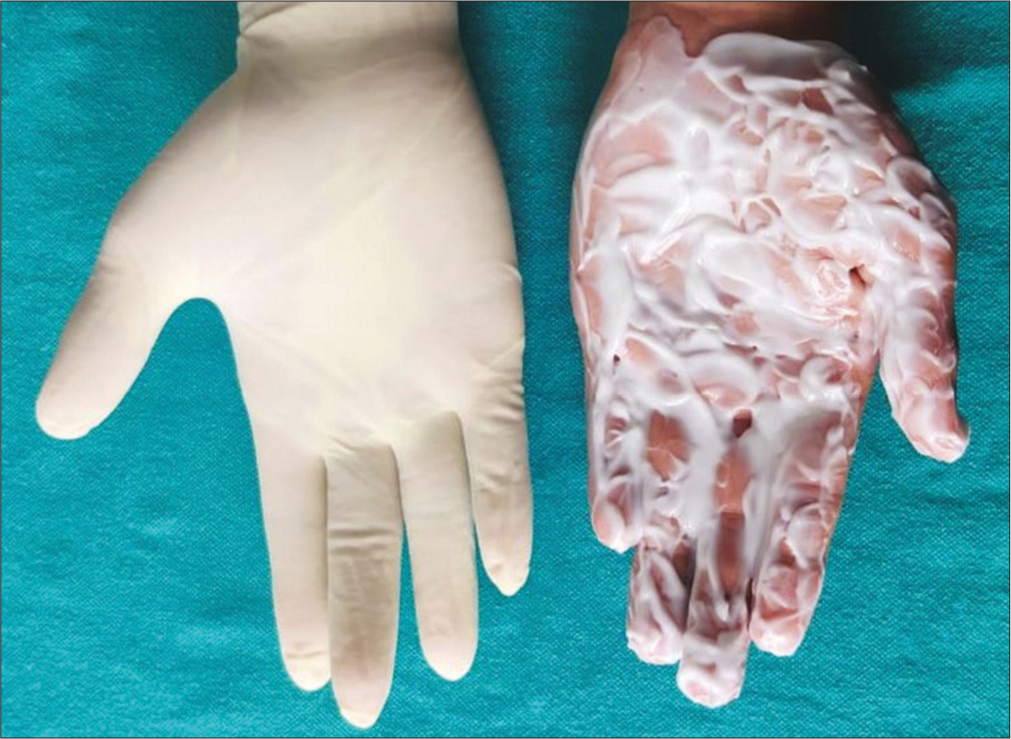
- Application of thick layer of lignocaine-prilocaine mixture followed by occlusion by double surgical gloves for two sessions of 1 hour each.
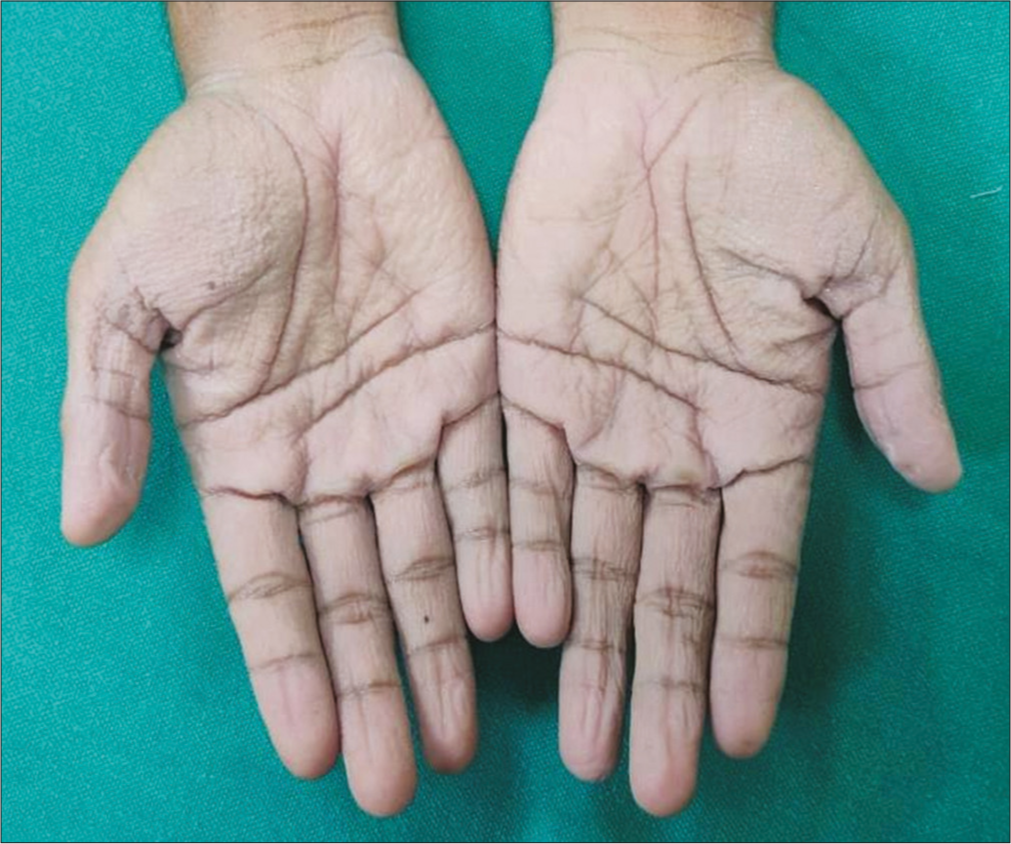
- Visible maceration of palmar surface achieved after 2 hours, which facilitates easy injection of botulinum toxin.
Authors’ contributions
All the authors contributed to the research study. Deepak Vashisht: Concepts, design, definition of intellectual content, literature search, manuscript preparation, manuscript editing, and manuscript review. Pankaj Das: Concepts, design, definition of intellectual content, literature search, manuscript preparation, manuscript editing, and manuscript review. S. Sampoorna Raj Choudhary: Concepts, design, definition of intellectual content, literature search, manuscript preparation, manuscript editing, and manuscript review. Gautam Kumar Singh: Concepts, design, definition of intellectual content, literature search, manuscript preparation, manuscript editing, and manuscript review. Preema Sinha: Concepts, design, definition of intellectual content, literature search, manuscript preparation, manuscript editing, and manuscript review. Amit Bahuguna: Concepts, design, definition of intellectual content, literature search, manuscript preparation, manuscript editing, and manuscript review. Devyani Sapra: Concepts, design, definition of intellectual content, literature search, manuscript preparation, manuscript editing, and manuscript review.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms. In the form, the patient(s) has/have given his/her/their consent for his/her/their images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal. The patients understand that their names and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.






