Translate this page into:
Use of syringe for atraumatic removal of milia
*Corresponding author: Ishan Agrawal, Department of Dermatology, Maulana Azad Medical College, New Delhi, India. ishanagrawal1995@gmail.com
-
Received: ,
Accepted: ,
How to cite this article: Azad MM O, Agrawal I, Ray A, Azad D. Use of syringe for atraumatic removal of milia. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. doi: 10.25259/jcas_141_23
Abstract
Milia extraction, typically done with a needle, risks inflammation and pigmentation from excessive manipulation. Using an insulin syringe needle allows for precise penetration and suction, efficiently extracting cyst contents with minimal skin trauma.
Keywords
Milia
Needle extraction
Suction
PROBLEM STATEMENT
Milia extraction is a frequently performed procedure in dermatology. The traditional approach involves using a needle to puncture the lesional surface and then carefully maneuvering it to extract the contents of the cyst. An inherent difficulty encountered during this process is the potential for excessive manipulation of the surrounding area, which can result in heightened local inflammation and persistent residual pigmentation.
RECOMMENDED SOLUTION
Utilizing the needle of an insulin syringe allows us to penetrate the Milia’s surface, and this apparatus functionally serves as an additional suction pump, effortlessly drawing out its contents without causing additional harm to the surrounding skin [Figure 1 and Video 1]. The merits of our approach encompass the following:
Significantly lower trauma risk, thereby minimizing the likelihood of excessive inflammation and residual pigmentation
Effortless extraction of milia bodies, particularly the smaller ones. Larger ones tend to rise to the skin’s surface and can be readily eliminated using gauze, obviating the need for the needle
This technique demands minimal expertise
No supplementary tools are necessary for the procedure.
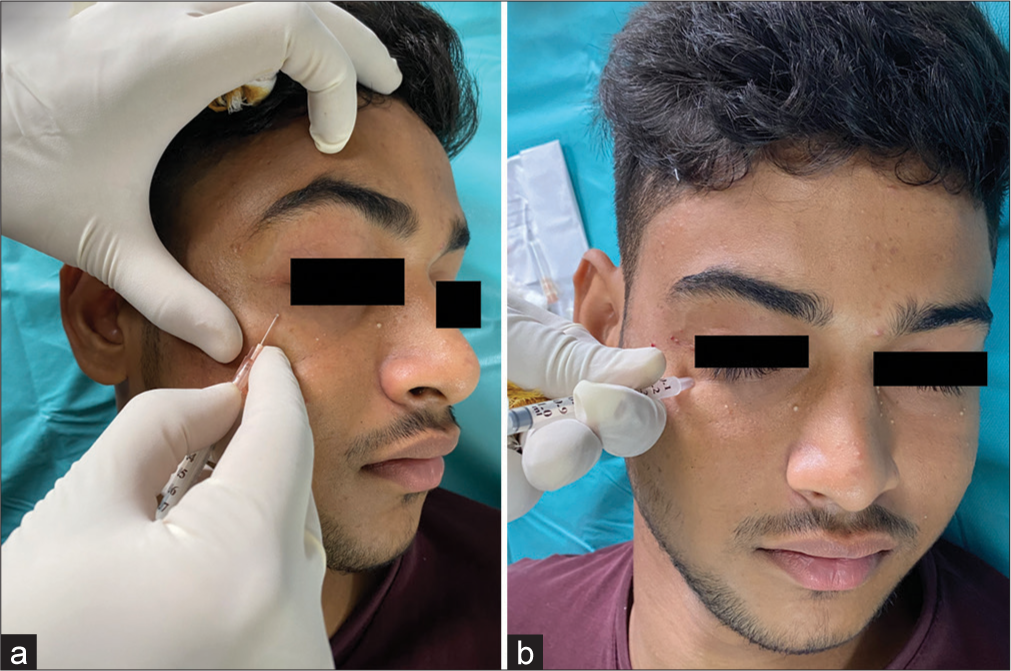
- Milia. (a) Insulin needle being used to penetrate the wall of Milia. (b) The syringe is used as a suction pump to draw the contents out.
Video 1:
Video 1:Demonstration of technique.Authors’ contributions
MM Omer Azad was responsible for conceptualization and manuscript design. Ishan Agrawal and Arunima Ray contributed to the manuscript writing and data collection. Darwin Azad and Arunima Ray reviewed and edited the manuscript.
Ethical approval
Institutional Review Board approval is not required.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for manuscript preparation
The authors confirm that there was no use of artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted technology for assisting in the writing or editing of the manuscript and no images were manipulated using AI.
Video available on:
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.







